Intestinal inflammation induces glymphatic remodeling, priming early neurodegenerative signals in male mice
- PMID: 41065132
- PMCID: PMC12509038
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.70640
Intestinal inflammation induces glymphatic remodeling, priming early neurodegenerative signals in male mice
Abstract
Introduction: Inflammatory bowel disease triggers extraintestinal manifestations, including in the central nervous system (CNS). However, the direct impact of peripheral inflammation on the CNS is largely unknown.
Methods: Using a mouse model of colitis with pain and anxiety-like behavior, we investigated the intricate pathogenic link between colonic inflammation, disruptions in circadian rhythmicity and impaired glymphatic circulation.
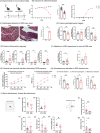
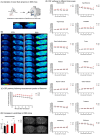
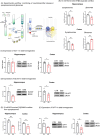
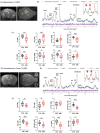
Results: By in vivo magnetic resonance imaging, we observed a derangement of brain fluid dynamics, with a significant enlargement of the cerebral lateral ventricles and waste deposition within the brain parenchyma. Proteomics revealed changes in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) composition, enriched in proteins related to inflammation, immune response, complement, neuronal, and lipid metabolic pathways. Alterations in brain metabolite concentrations and in inhibitory control mechanisms and excitatory transmission were detected.
Discussion: Colonic inflammation induces remodeling in CSF volume distribution, clearance, and metabolism, with derangement of the crosstalk between neurons and astrocytes, priming synaptopathy.
Highlights: An acute peripheral inflammatory trigger affects the central level by remodeling central nervous system (CNS) fluid distribution and priming early signals of synaptopathy. A single dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) challenge disrupts the circadian clock machinery and alters CNS fluid distribution, a so far neglected system, thereby impairing glymphatic clearance of waste products and indirectly altering neurotransmitter release dynamics. These combined effects ultimately impact brain function, extending to the regulation of behavior. Understanding how an intestinal inflammatory insult may derange the daily rhythm of the mechanisms controlling brain waste disposal may help identify specific groups of subjects at high risk of developing neurological disorders.
Keywords: aquaporin‐4; brain waste clearance; circadian regulation; dextran sulfate sodium–driven painful colitis; inflammation; neurotransmitter release.
© 2025 The Author(s). Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests. Author disclosures are available in the supporting information.
Figures



References
-
- Zong J, Yang Y, Wang H, Zhang H, Yang X, Yang X. The two‐directional prospective association between inflammatory bowel disease and neurodegenerative disorders: a systematic review and meta‐analysis based on longitudinal studies. Front Immunol. 2024;15:1325908. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1325908 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Talley S, Valiauga R, Anderson L, Cannon AR, Choudhry MA, Campbell EM. DSS‐induced inflammation in the colon drives a proinflammatory signature in the brain that is ameliorated by prophylactic treatment with the S100A9 inhibitor paquinimod. J Neuroinflammation. 2021;18:263. doi: 10.1186/s12974-021-02317-6 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

