HIF-2-Dependent Regulation of PTHrP and Paraneoplastic Hypercalcemia in Aggressive Clear-Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 41065553
- PMCID: PMC12642454
- DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-25-0638
HIF-2-Dependent Regulation of PTHrP and Paraneoplastic Hypercalcemia in Aggressive Clear-Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
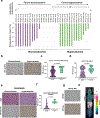
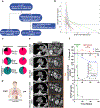
Patients with renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and hypercalcemia (HC) have worse outcomes. HC often involves parathyroid hormone-related protein (PTHrP), and the role of hypoxia-inducible factor 2 (HIF-2) is incompletely understood. Leveraging RCC tumorgraft (TG) models of HC, which were characterized by tumor cell-autonomous inflammatory/immune signatures, we show that HIF-2 inhibition with PT2399 frequently normalized calcium, downregulated circulating PTHrP, and reduced HIF-2 binding to the PTHLH (PTHrP) promoter. Likely contributing to the selective induction of PTHrP in a subset of HIF-2-dependent tumors, the PTHLH locus was generally more accessible in TG(HC). However, PTHLH chromatin accessibility was grossly unaffected by PT2399, unlike elsewhere (including the EPO locus in a TG with paraneoplastic polycythemia). As in TGs, paraneoplastic HC in patients was associated with clear-cell (cc)RCC (and sarcomatoid/rhabdoid differentiation) and was rapidly corrected by PT2977/belzutifan, which unlike bisphosphonates downregulated PTHrP. Our data support evaluating HIF-2 antagonists for ccRCC patients with paraneoplastic HC, which may serve as a predictive biomarker.
Significance: This study uncovers a direct role for HIF-2 in driving humoral HC of malignancy in ccRCC through transcriptional activation of PTHLH (encoding PTHrP), identifies HC (and PTHrP) as potentially predictive biomarkers of HIF-2 engagement, and sets a foundation for the evaluation of HIF-2 antagonists for HC management in patients.
©2025 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



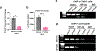

References
-
- Heng DY, Xie W, Regan MM, Warren MA, Golshayan AR, Sahi C, et al. Prognostic factors for overall survival in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted agents: results from a large, multicenter study. J Clin Oncol 2009;27(34):5794–9 doi 10.1200/JCO.2008.21.4809. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U54 CA224065/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA245294/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK127984/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA295997/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA196516/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA070907/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RP230382/Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas (CPRIT)
- RP240516/Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas (CPRIT)
- HT9425-25-1-0346/Congressionally Directed Medical Research Programs (CDMRP)
- P50CA196516/National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- R01CA245294/National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- R01CA295997/National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- P50CA196516/National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- P50CA070907/National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- U54 CA224065/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30DK127984/National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

