Platelets impair the resolution of inflammation in atherosclerotic plaques in insulin-resistant mice after lipid lowering
- PMID: 41066197
- PMCID: PMC12643486
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.193593
Platelets impair the resolution of inflammation in atherosclerotic plaques in insulin-resistant mice after lipid lowering
Abstract
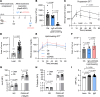
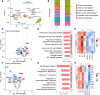
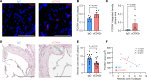
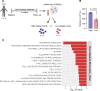
Insulin resistance impairs benefits of lipid-lowering treatment, as evidenced by higher cardiovascular disease risk in individuals with type 2 diabetes versus those without. Because platelet activity is higher in insulin-resistant patients and promotes atherosclerosis progression, we questioned whether platelets impair inflammation resolution in plaques during lipid lowering. In mice with obesity and insulin resistance, we induced advanced plaques and then implemented lipid lowering to promote atherosclerotic plaque inflammation resolution. Concurrently, mice were treated with either platelet-depleting or control antibodies for 3 weeks. Platelet activation and insulin resistance were unaffected by lipid lowering. Both antibody-treated groups showed reduced plaque macrophages, but plaque cellular and structural composition differed. In platelet-depleted mice, single-cell RNA-seq revealed dampened inflammatory gene expression in plaque macrophages and an expansion of a subset of Fcgr4+ macrophages having features of inflammation-resolving, phagocytic cells. Necrotic core size was smaller and collagen content greater, resembling stable human plaques. Consistent with the mouse results, clinical data showed that patients with lower platelet counts had decreased proinflammatory signaling pathways in circulating nonclassical monocytes after lipid lowering. These findings highlight that platelets hinder inflammation resolution in atherosclerosis during lipid-lowering treatment. Identifying novel platelet-targeted therapies following lipid-lowering treatment in individuals with insulin resistance may be a promising therapeutic approach to promote atherosclerotic plaque inflammation resolution.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Cardiology; Diabetes; Inflammation; Platelets; Vascular biology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Huang YT, et al. Efficacy and safety of proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 Inhibitors as adjuvant treatments for patients with hypercholesterolemia treated with statin: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:832614. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.832614. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

