SMC modulates ParB engagement in segregation complexes in streptomyces
- PMID: 41068141
- PMCID: PMC12511625
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-64044-3
SMC modulates ParB engagement in segregation complexes in streptomyces
Abstract
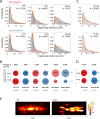
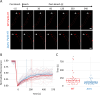
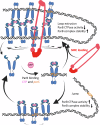
ParB is a bacterial chromosome segregation protein with recently demonstrated CTPase activity. CTP-bound ParB homodimers are loaded onto DNA at parS sites and spread along DNA, forming a large nucleoprotein complex. ParB complexes recruit condensin (SMC protein). Whether SMC modulates ParB complexes has remained unknown. Here, we employ Streptomyces venezuelae strains producing ParB-HaloTag in the presence or absence of SMC and use single-cell time-lapse fluorescence microscopy, single molecule tracking and fluorescence recovery after photobleaching analyses to explore ParB dynamics. Additionally, we perform chromatin immunoprecipitation to examine ParB interactions with DNA, with or without SMC. We reveal that SMC modulates ParB complex stability and ParB mobility. We find that the absence of SMC reduces ParB spreading. Additionally, we show that SMC reduces ParB CTPase activity in vitro. Taken together our data provide evidence of SMC positive feedback on the ParB nucleoprotein complex, offering insight into the nature of ParB complexes.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Breier, A. M. & Grossman, A. D. Whole-genome analysis of the chromosome partitioning and sporulation protein Spo0J (ParB) reveals spreading and origin-distal sites on the Bacillus subtilis chromosome. Mol. Microbiol.64, 703–718 (2007). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

