Advances in RNA-based cancer therapeutics: pre-clinical and clinical implications
- PMID: 41068915
- PMCID: PMC12512572
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-025-02463-y
Advances in RNA-based cancer therapeutics: pre-clinical and clinical implications
Abstract
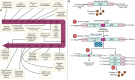
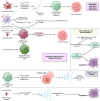
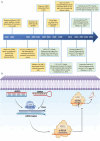
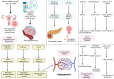
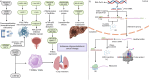
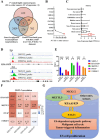
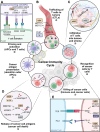
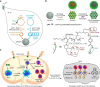
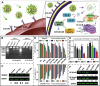
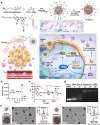
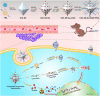
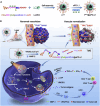
Cancer therapy has been revolutionised by the emergence of RNA-based therapeutics, providing several strategies and mechanisms to regulate gene expression via messenger RNA (mRNA), small interfering RNA (siRNA), microRNAs (miRNA), antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs), and RNA aptamers. The present review highlights the recent advances in the preclinical development and clinical applications of RNA-based therapeutics, focusing on the delivery strategies, biological targets, and pharmacological optimisation, together with key clinical data. mRNA therapeutics, especially those adapted from vaccine platforms are being developed for the cancer immunotherapy and protein replacement, while siRNAs and ASOs enable highly specific gene silencing and splice correction. miRNA therapies show potential for diverse oncogenic pathway control, despite ongoing challenges in the delivery and specificity. RNA aptamers are obtaining attention as tumor-targeting agents in the drug delivery systems. Progress in lipid nanoparticles, chemical modifications, and tissue-specific delivery has improved the stability and efficacy of these agents. Early-phase clinical trials report encouraging outcomes in both solid tumours and haematologic malignancies, particularly in overcoming resistance and modulating the tumor microenvironment (TME). Although challenges remain in scalability, immune activation, and deep-tumour penetration, RNA-based strategies are advancing towards integration into clinical oncology. Continued refinement of delivery technologies and targeted trial designs will be critical for translating these therapies into effective, personalized cancer treatments.
Keywords: Antisense oligonucleotides; Cancer immunotherapy; MRNA vaccine; RNA aptamers; SiRNA.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

