The Bleeding Disorders Research Collaborative
- PMID: 41070002
- PMCID: PMC12506547
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bvth.2025.100099
The Bleeding Disorders Research Collaborative
Abstract
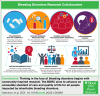
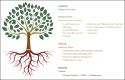
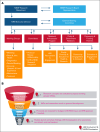
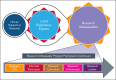
The Bleeding Disorders Research Collaborative (BDRC) aims to advance an accessible standard of care and quality of life for all people living with inheritable bleeding disorders. This goal will be achieved through collaborative and meaningful scientific inquiry, coordinated by an efficient research infrastructure, and undertaken by a diverse, capacitated workforce in partnership with an engaged community. The BDRC is supported by facilitative research policy and grounded in the principles of health equity, diversity, inclusion, accessibility, and belonging, striving for dignity, safety, well-being, and opportunities, leading to health justice. Importantly, the initiative is fully informed by lived experience experts, people affected by inheritable bleeding disorders, who are key members in the research development, implementation, and dissemination team.
© 2025 American Society of Hematology. Published by Elsevier Inc. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: L.A.V. reports honoraria and travel support from Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc for speaking; and consulting fees from Inovio, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc, Sanofi, and Takeda. M.E.S., M.R., and H.B. are employees of National Bleeding Disorders Foundation (NBDF). M.L.W. was an employee of NBDF at the time this work was performed. D.D. is a paid consultant to NBDF, the American Society of Hematology, and Believe Limited LLC. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures



References
-
- Mainz J, Kristensen S, Roe D. The power of the patient's voice in the modern health care system. Int J Qual Health Care. 2022;34(suppl 1):ii1–ii2. - PubMed
-
- Jacob J. Voice of the patient: the essence of patient-centered care. Crit Care Nurs Clin North Am. 2010;22(2):227–232. - PubMed
-
- Bruch JD, Khazen M, Mahmic-Kaknjo M, Légaré F, Ellen ME. The effects of shared decision making on health outcomes, health care quality, cost, and consultation time: an umbrella review. Patient Educ Couns. 2024;129 - PubMed
-
- Vázquez E, Kim M, Santaella ME. Lived experience experts: a name created by us for us. Expert Rev Hematol. 2023;16(suppl 1):7–11. - PubMed
-
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration FDA-led patient-focused drug development (PFDD) public meetings. https://www.fda.gov/industry/prescription-drug-user-fee-amendments/fda-l...
