Musculoskeletal manifestations in children with inflammatory bowel disease: a multicenter cohort study (GASTROREUM study)
- PMID: 41074165
- PMCID: PMC12512456
- DOI: 10.1186/s12969-025-01141-z
Musculoskeletal manifestations in children with inflammatory bowel disease: a multicenter cohort study (GASTROREUM study)
Abstract
Background: Musculoskeletal (MSK) symptoms are the most common extra-articular manifestations of pediatric-onset inflammatory bowel diseases (pIBD), and are associated with a more aggressive disease course. This study aims to characterize MSK manifestations in patients with pIBD, and to seek for predictors of persistently active arthritis one year after pIBD diagnosis.
Methods: A multicenter, retrospective cohort study was conducted at 25 Italian pediatric rheumatology centers. Patients aged < 18 years with pIBD and MSK manifestations, followed for at least one year, were included. Data at onset of first MSK symptom, pIBD diagnosis, and one-year follow-up visit following pIBD diagnosis were collected.
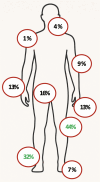
Results: A total of 180 patients were included, 111 (61.7%) with Crohn’s disease (CD), 55 (30.5%) with ulcerative colitis (UC), and 14 (7.8%) with unclassified IBD (IBDU). Arthralgia (72.8%) and arthritis (69.4%), were the most frequent MSK manifestations. Patients with CD had MSK symptoms prior to pIBD diagnosis more frequently than those with UC/IBDU (51.4% vs. 40.6%). Among the 125 patients with arthritis, 76.8% had peripheral arthritis, 14.4% had axial disease, and 8.8% had both peripheral and axial involvement. The most common articular pattern was oligoarthritis (52.0%), followed by monoarthritis (26.4%) and polyarthritis (21.6%). The most frequently affected joints were the knee, ankle, and hip. On multivariable analysis, antinuclear antibody (ANA) positivity (OR = 3.05, 95% CI: 1.05 – 8.89) and a polyarticular course of arthritis (OR = 3.42, 95% CI: 1.13–10.38) were independently associated with persistence of active arthritis at year 1 after pIBD diagnosis.
Conclusions: Most patients with pIBD and arthritis presented with peripheral oligoarthritis affecting lower limb joints. A positive ANA status and development of polyarthritis predicted sustained arthritis activity.
Supplementary Information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s12969-025-01141-z.
Keywords: Antinuclear antibodies; Arthritis; Children; Inflammatory bowel disease; Juvenile idiopathic arthritis; Musculoskeletal; Sacroiliitis.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of [ASL Lecce, Italy (codex REUMAPED—28 August 2022)]. Consent for publication: Written informed consent was obtained from all participants and/or their legal guardians prior to enrollment. Competing interests: Co-Editor-in-Chief Angelo Ravelli is on the author list.
Figures
References
-
- Müller KE, Lakatos PL, Arató A, Kovács JB, Várkonyi Á, Szűcs D, et al. Incidence, Paris classification, and follow-up in a nationwide incident cohort of pediatric patients with inflammatory bowel disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2013;57(5):576–82. 10.1097/MPG.0b013e31829f7d8c. - PubMed
-
- Greuter T, Bertoldo F, Rechner R, Straumann A, Biedermann L, Zeitz J, et al. Extraintestinal manifestations of pediatric inflammatory bowel disease: prevalence, presentation, and anti-TNF treatment. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2017;65(2):200–6. 10.1097/MPG.0000000000001455. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources