End-to-end deep learning model for the diagnosis and segmentation of primary retroperitoneal neoplasm: a multicenter cohort study
- PMID: 41079030
- PMCID: PMC12508580
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2025.103498
End-to-end deep learning model for the diagnosis and segmentation of primary retroperitoneal neoplasm: a multicenter cohort study
Abstract
Background: Primary retroperitoneal neoplasms (PRNs) are a diverse group of tumors that pose significant diagnostic challenges. Currently, no multicenter-validated diagnostic model exists for multiple PRN types based on computed tomography (CT) images. This study aimed to develop and validate an end-to-end deep learning model, REMIND (REtroperitoneal neoplasMs artificial-INtelligence Diagnosis), for the accurate diagnosis and segmentation of PRNs using enhanced CT images.
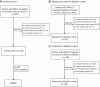
Methods: Patients from 12 Chinese centers between January 2012 and June 2024 were involved in this study. The dataset comprised patients with histologically confirmed PRNs, including seven types of PRNs: dedifferentiated liposarcoma, well-differentiated liposarcoma, leiomyosarcoma, ganglioneuroma, lymphoma, schwannoma, and paraganglioma. The REMIND model was trained using retrospective data from a single hospital in China (n = 606; five-fold cross validation), and externally validated using retrospectively collected data from 11 different hospitals (n = 736) and prospectively validated using prospectively collected data from the same hospital as the training set (n = 188) enrolled from January 2024 to June 2024. Additionally, a reader study involving 30 radiologists from 11 hospitals in China was conducted to assess REMIND's clinical utility.
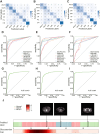
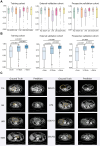
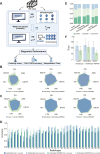
Findings: REMIND demonstrated high predictive accuracy across different cohorts. For classifying neoplasm types, ROC curves showed AUCs over 0.80 for most types. For 7-way classification task, REMIND achieved top-1 accuracies of 0.66 (95%CI 0.61-0.69), 0.61 (95%CI 0.46-0.73), 0.63 (95%CI 0.54-0.69), and top-2 accuracies of 0.82 (95%CI 0.79-0.85), 0.79 (95%CI 0.77-0.83), 0.77 (95%CI 0.71-0.83) in the training, external validation, and prospective validation cohorts, respectively. For segmentation tasks, REMIND achieved average Dice scores of 0.75 (95%CI 0.73-0.76), 0.72 (95%CI 0.70-0.74), and 0.73 (95%CI 0.70-0.77) in training, external validation, and prospective validation cohorts. The reader study indicated the top-1 classification accuracy of REMIND was higher than junior radiologists (64.0% vs. 42.6%, p = 0.006), and attending radiologists (64.0% vs. 57.4%, p = 0.009) and equivalent to senior radiologists (64.0% vs. 64.3%, p = 0.905). When assisted by REMIND, the diagnostic accuracy of junior and attending radiologists significantly improved. Meanwhile, REMNID reduced interpretation time and increased diagnostic certainty in all groups of radiologists.
Interpretation: REMIND represents a first-in-class model for the diagnosis and segmentation of PRNs. Its integration into clinical practice has the potential to enhance diagnostic accuracy, increase predictive certainty, and reduce interpretation time. This study highlights the clinical applicability of AI in improving the diagnostic accuracy and reducing the workload for radiologists handling these rare and complex tumors.
Funding: This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82272905 and 82473385).
Keywords: Computed tomography; Deep-learning; Diagnosis; Liposarcoma; Primary retroperitoneal neoplasms; Segmentation.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Sangster G.P., Migliaro M., Heldmann M.G., Bhargava P., Hamidian A., Thomas-Ogunniyi J. The gamut of primary retroperitoneal masses: multimodality evaluation with pathologic correlation. Abdom Radiol. 2016;41:1411–1430. - PubMed
-
- Osman S., Lehnert B.E., Elojeimy S., et al. A comprehensive review of the retroperitoneal anatomy, neoplasms, and pattern of disease spread. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2013;42:191–208. - PubMed
-
- Villano A.M., Zeymo A., Chan K.S., Unger K.R., Shara N., Al-Refaie W.B. Variations in retroperitoneal soft tissue sarcoma outcomes by hospital type: a national cancer database analysis. JCO Oncol Pract. 2020;16:e991–e1003. - PubMed
-
- Bonvalot S., Gronchi A., Le Péchoux C., et al. Preoperative radiotherapy plus surgery versus surgery alone for patients with primary retroperitoneal sarcoma (EORTC-62092: STRASS): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020;21:1366–1377. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

