Factors influencing multidisciplinary clinical decision-making in the critical care unit: a systematic review and mixed-methods meta-synthesis
- PMID: 41079521
- PMCID: PMC12509128
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bjao.2025.100488
Factors influencing multidisciplinary clinical decision-making in the critical care unit: a systematic review and mixed-methods meta-synthesis
Abstract
Background: The intensive care unit (ICU) is a dynamic environment that necessitates daily clinical decisions regarding organ support treatments. The decision-making process varies significantly between clinicians (i.e. doctors, nurses, and allied healthcare practitioners), even where internationally accepted treatment guidance exists. The factors and the processes influencing clinical decision-making are poorly understood. This systematic review aims to generate a decision-making model by evaluating current evidence on the decision-making process and the factors that affect decisions on organ support treatments in the ICU.
Methods: We conducted a systematic search on three databases (PubMed, Embase, and CINAHL) including all papers exploring factors that influenced organ support decisions (PROSPERO: CRD42021283290). A mixed-methods meta-synthesis was performed to enable the generation of distinct themes and subthemes used to generate the decision-making model.
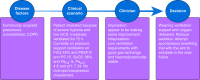
Results: After screening 8967 records, 33 studies met the inclusion criteria and were included in the analysis. The mixed-method interpretation of the data found that decision-making can be linear and primarily dictated by patient factors (i.e. patient's clinical parameters). However, the analysis identified 11 factors that can influence and strain clinician's decision-making. Four themes: 1) human, 2) team, 3) system, and 4) patient emerged as the potential modifiable factors to optimise the decision-making process.
Conclusions: Decision-making surrounding organ support treatment is complex and dynamic. However, there are four distinctive potentially modifiable themes that influence the multidisciplinary decision-making process. Further studies should focus on understanding interventions to improve decision-making and if different decision-making processes directly affect patients' outcomes.
Systematic review protocol: PROSPERO (CRD42021283290).
Keywords: complex decisions; decision model; decision-making; multidisciplinary; organ support.
Crown Copyright © 2025 Published by Elsevier Ltd on behalf of British Journal of Anaesthesia.
Conflict of interest statement
TS reports receiving salary support from the Barts Charity (London, UK) for this study. All other authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Gambrill E.D. 1st Edn. Jossey-Bass Publishers; San Francisco: 1990. xvii. Critical Thinking in Clinical Practice : Improving the Accuracy of Judgments and Decisions About Clients; p. 432.
-
- Alexis Ruiz A., Wyszynska P.K., Laudanski K. Narrative review of decision-making processes in critical care. Anesth Analg. 2019;128:962–970. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

