Ultrafast in situ formed robust and adhesive photo-crosslinked hydrogel encapsulating curcumin for ulcerative colitis alleviation via regulating inflammation and gut microbiota
- PMID: 41080726
- PMCID: PMC12513075
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.102312
Ultrafast in situ formed robust and adhesive photo-crosslinked hydrogel encapsulating curcumin for ulcerative colitis alleviation via regulating inflammation and gut microbiota
Abstract
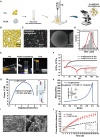
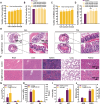
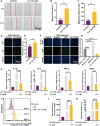
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a chronic, relapsing-remitting inflammatory condition that primarily affects the colonic mucosa. Its treatment is significantly constrained by the systemic side effects of non-specific drugs like glucocorticoids. Curcumin (Cur) is known as a safe and potent compound for mitigating UC, but its application is hindered by low colonic bioavailability. Hydrogel presents a promising colonic delivery system for drugs to reduce side effects and enhance colonic bioavailability. However, achieving hydrogel adhesion and stability in the harsh colonic environment is quite challenging. Here, to overcome these challenges, we have developed an adhesive and robust photo-crosslinked hydrogel encapsulated with Cur loaded poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) microspheres (Cur@PLGA-Gel) for effective UC alleviation. The pre-gel solution can be delivered into the colon to form a tough hydrogel with strong tissue adhesion via the photo-triggered transient radical and persistent radical coupling (PTPC) reaction, enabling colonic retention of Cur for over 72 h. Moreover, PLGA enhances the stability, solubility and dispersibility of Cur. Through the integration of in vivo and in vitro approaches, we have confirmed that Cur@PLGA-Gel can promote cell proliferation, eliminate reactive oxygen species (ROS), and regulate immune responses and gut microbiota balance, thereby effectively alleviating UC symptoms. Collectively, this study provides an effective and safe strategy for UC treatment.
Keywords: Adhesive; Curcumin; Photo-crosslinked hydrogel; Ulcerative colitis; Ultrafast.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures







References
-
- Ng S.C., Shi H.Y., Hamidi N., Underwood F.E., Tang W., Benchimol E.I., Panaccione R., Ghosh S., Wu J.C.Y., Chan F.K.L., Sung J.J.Y., Kaplan G.G. Worldwide incidence and prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease in the 21st century: a systematic review of population-based studies. Lancet. 2017;390:2769–2778. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(17)32448-0. - DOI - PubMed
