Macrophage-Engaging IgG4 Antibody Triggers Cytotoxicity against Integrin αvβ3+ Cancers
- PMID: 41081633
- PMCID: PMC12570272
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-25-0300
Macrophage-Engaging IgG4 Antibody Triggers Cytotoxicity against Integrin αvβ3+ Cancers
Abstract
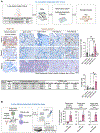
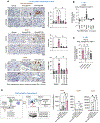
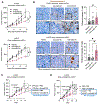
Integrin αvβ3, absent in most normal cells, has emerged as both a marker and a driver of tumor stemness and drug resistance in epithelial cancers, making it an attractive therapeutic target. The humanized IgG1 anti-αvβ3 antibody etaracizumab was originally developed to exploit NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity against αvβ3-positive tumors. However, despite its favorable safety profile and clinical efficacy, its impact was insufficient for further development. We previously discovered that αvβ3-positive epithelial tumors exhibit a tumor-associated macrophage (TAM)-rich microenvironment with limited NK-cell infiltration, potentially limiting the effectiveness of etaracizumab. In this study, we hypothesized that re-engineering the anti-αvβ3 antibody to activate TAM-mediated cytotoxicity would enhance its antitumor activity. We developed a fully human IgG4 variant of etaracizumab (anti-αvβ3 G4) with identical affinity for integrin αvβ3, but optimized for activation of CD64, an immune effector cell-activating receptor, selectively expressed on macrophages. In organotypic cultures of patients with lung cancer and mouse lung cancer xenografts, anti-αvβ3 G4 demonstrated superior antitumor activity compared with its IgG1 counterpart. Mechanistically, this enhancement was driven by CD64 activation in TAMs, leading to robust upregulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase, a pivotal enzyme for immune effector-mediated cytotoxicity. Our findings reveal a powerful strategy for targeting highly aggressive, drug-resistant integrin αvβ3-positive tumors by harnessing TAMs for antibody-mediated cancer therapy and demonstrate that this Fc switch approach may be broadly applicable to other targets in TAM-enriched tumor microenvironments.
©2025 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Seguin L, Kato S, Franovic A, Camargo MF, Lesperance J, Elliott KC, Yebra M, Mielgo A, Lowy AM, Husain H, Cascone T, Diao L, Wang J, Wistuba II, Heymach JV, Lippman SM, Desgrosellier JS, Anand S, Weis SM, Cheresh DA. An integrin β3-KRAS-RalB complex drives tumour stemness and resistance to EGFR inhibition. Nat Cell Biol. 2014;16(5):457–68. Epub 20140420. doi: 10.1038/ncb2953. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Seguin L, Camargo MF, Wettersten HI, Kato S, Desgrosellier JS, von Schalscha T, Elliott KC, Cosset E, Lesperance J, Weis SM, Cheresh DA. Galectin-3, a Druggable Vulnerability for KRAS-Addicted Cancers. Cancer Discov. 2017;7(12):1464–79. Epub 20170911. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-17-0539. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
- K01 OD030513/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA023100/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK120515/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS047101/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K01OD030513/National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- DD2204/San Diego Digestive Diseases Research Center, School of Medicine, University of California, San Diego (SDDRC)
- FA1-00607/California Institute for Regenerative Medicine (CIRM)
- NS047101/National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- P30DK120515/National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- P30CA23100/National Institutes of Health (NIH)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

