Apomorphine is a novel necroptosis inhibitor targeting mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein oligomerization
- PMID: 41083456
- PMCID: PMC12518639
- DOI: 10.1038/s41420-025-02763-8
Apomorphine is a novel necroptosis inhibitor targeting mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein oligomerization
Abstract
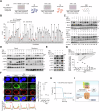
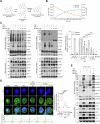
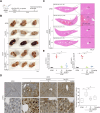
Necroptosis, a form of programmed cell death, has emerged as a promising therapeutic target. Although several RIPK1 inhibitors have demonstrated favorable safety profiles in clinical trials, clinical translation of necroptosis-targeted therapies remains limited by modest efficacy, limited specificity, and species-specific activity of compounds such as necrosulfonamide (NSA). To resolve these challenges, this study identified a potential necroptosis inhibitor from a clinical drug library. Apomorphine (APO), a non-addictive morphine derivative used to treat Parkinson's disease, was found to inhibit necroptosis by sterically blocking key residues involved in mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein (MLKL) activation and oligomerization, as confirmed by nuclear magnetic resonance analysis. APO is redox sensitive and prone to auto-oxidation. The oxidized form of APO (Ox-APO) showed stronger binding to MLKL than the reduced form of APO (Re-APO), as demonstrated by surface plasmon resonance analysis. Ox-APO significantly ameliorated tissue damage in two murine necroptosis models: dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis and acetaminophen (APAP)-induced liver injury. Collectively, these data highlight the therapeutic potential of APO as a necroptosis-specific inhibitor in necroptosis-related diseases in both humans and mice.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical approval and consent to participate: All methods were performed in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations. C57BL/6 and BALB/c mice were used following procedures approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of the Yonsei Laboratory Animal Research Center (YLARC, 2018-0024). MLKL–/– C57BL/6 mice were used following procedures approved by the IACUC of the Laboratory Animal Research Center (LARC) of Ajou University Medical Center (2023-0053). No human participants were involved in this study; therefore, informed consent was not required.
Figures


References
-
- Degterev A, Huang Z, Boyce M, Li Y, Jagtap P, Mizushima N, et al. Chemical inhibitor of nonapoptotic cell death with therapeutic potential for ischemic brain injury. Nat Chem Biol. 2005;1:112–9. - PubMed
-
- Kim YS, Morgan MJ, Choksi S, Liu ZG. TNF-induced activation of the Nox1 NADPH oxidase and its role in the induction of necrotic cell death. Mol Cell. 2007;26:675–87. - PubMed
-
- Sun L, Wang H, Wang Z, He S, Chen S, Liao D, et al. Mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein mediates necrosis signaling downstream of RIP3 kinase. Cell. 2012;148:213–27. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

