Neuron-targeted ROS-responsive liposomes for puerarin delivery remodel ischemic microenvironment via microglial modulation and neurovascular regeneration
- PMID: 41084040
- PMCID: PMC12519847
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-025-03730-2
Neuron-targeted ROS-responsive liposomes for puerarin delivery remodel ischemic microenvironment via microglial modulation and neurovascular regeneration
Abstract
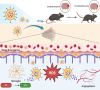
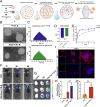
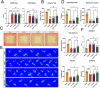
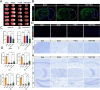
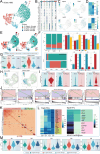
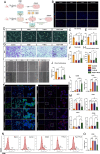
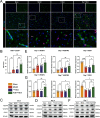
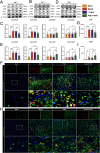
Ischemic stroke triggers the "ischemic cascade," which encompasses vascular injury, oxidative stress, inflammatory responses, and mitochondrial dysfunction, ultimately leading to neuronal death and impaired brain function. Conventional pharmacotherapies have specific limitations, such as being restricted by the blood-brain barrier (BBB), causing systemic side effects, and having poor lesion targeting. To tackle the aforementioned challenges, this study developed PUELipo/R-R, a safe and highly biocompatible liposome nanocarrier modified with reactive oxygen species (ROS)-responsive DSPE-TK-PEG and neuron-targeting RVG29 peptide on the surface, for the precise delivery of puerarin (PUE) to ischemic brain regions and the release of stimuli-responsive drugs. PUE demonstrates the advantage of multi-target regulation in treating ischemic stroke. In a mouse model of middle cerebral artery occlusion/reperfusion (MCAO/r), PUELipo/R-R significantly reduced the volume of cerebral infarction, decreased neuronal death rate, and improved post-stroke motor function. The results of single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) revealed that endothelial cells (ECs) and microglia were the cell types with the most significant alterations in the experimental group treated with PUELipo/R-R. Both in vitro and in vivo studies have verified that PUELipo/R-R enhances the expression levels of angiogenesis-related factors, promotes the proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis of cerebrovascular ECs, and improves neuroinflammatory conditions by facilitating the transformation of microglia from the pro-inflammatory M1 phenotype to the anti-inflammatory M2 phenotype. This novel multi-target therapeutic strategy highlights the potential application of PUELipo/R-R as a possible treatment for ischemic stroke and related disorders.
Keywords: Cerebral ischemia; Liposome; Microglia polarization; Neuron-targeting; Neurovascular regeneration; Puerarin; ROS-responsive.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

