Incidental Discovery of a Chronically Dissected Pulmonary Artery
- PMID: 41084676
- PMCID: PMC12515108
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.92095
Incidental Discovery of a Chronically Dissected Pulmonary Artery
Abstract
Pulmonary artery dissection is a rare and potentially fatal vascular emergency most often associated with pulmonary hypertension. In this report, we describe the incidental discovery of a chronically dissected pulmonary artery in a 92-year-old woman who presented to the emergency department with abdominal discomfort, constipation, and poor appetite. Imaging to evaluate for occult malignancy revealed a dissection flap within the main pulmonary artery and findings suggestive of chronicity. These radiographic findings included parenchymal scarring of the left lung, calcification, and collateralization of pulmonary vessels. Given the patient's age and lack of symptoms, no invasive treatment approach was pursued after multidisciplinary discussion. Classically considered a deadly disease, pulmonary artery dissection may not be as universally fatal as once thought and may present subclinically, remaining undetected for extended periods of time. Early recognition of atypical and indolent presentations is essential, especially in an era of widespread cross-sectional imaging and in patients for whom invasive intervention may not be appropriate.
Keywords: chronic dissection; chronic pulmonary hypertension; internal med; pulmonary artery dissection; pulmonary critical care; pulmonary trunk.
Copyright © 2025, Lee et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Informed consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
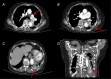
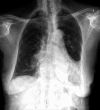
References
-
- Pulmonary artery dissection: a case treated by homograft replacement. Adodo DK, Kloeckner M, Bergoend E, Couëtil JP. Ann Thorac Surg. 2017;103:0–9. - PubMed
-
- Fatal dissection of the pulmonary artery in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Degano B, Prevot G, Têtu L, Sitbon O, Simonneau G, Humbert M. Eur Respir Rev. 2009;18:181–185. - PubMed
-
- Transthoracic echocardiographic findings of pulmonary artery dissection. Li RJ, Yang Y, Zhang XS, Li ZA. J Ultrasound Med. 2010;29:1365–1368. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
