A randomized trial of two online platforms for dementia family caregivers: GamePlan4Care and Resources4Care
- PMID: 41085219
- PMCID: PMC12519501
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.70690
A randomized trial of two online platforms for dementia family caregivers: GamePlan4Care and Resources4Care
Abstract
Introduction: Digital technologies can increase the accessibility of evidence-based caregiver programs.
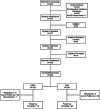
Methods: A 6-month, phase I, exploratory, randomized-controlled trial of two dementia caregiver support platforms, GamePlan4Care (GP4C) and Resources4Care (R4C), each enrolling 120 community-based family caregivers. Outcome measures included burden, positive aspects of caregiving, social support, and depression.
Results: Caregivers showed significant follow-up improvements in burden (GP4C: effect size [ES] = 0.50, p < 0.001; R4C: ES = 0.47, p < 0.001), positive aspects of caregiving (GP4C: ES = 0.26, p = 0.022; R4C: ES = 0.23, p = 0.030), social support (GP4C: ES = 0.21, p = 0.035), and distress (GP4C: ES = 0.30, p = 0.010). Caregivers engaged more in GP4C (GP4C: mean 5.5 h, SD = 0.61; R4C: mean 1.9 h, SD = 0.20) and set more goals for the safety domain (mean 8.9 goals, SD = 7.60).
Discussion: GP4C was not superior to R4C; however, both platforms demonstrated improved outcomes. Findings highlight a health system's successful development and implementation of online dementia caregiver platforms. Improving digital technology for caregivers requires studies with larger populations and longitudinal outcomes.
Trial registration number: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT04540198 HIGHLIGHTS: Online platforms can be useful in the goal of supporting family caregivers with educational and skills-training material to reduce the negative consequences of caregiving and to improve positive feelings of caregiving. Rules-based conditional logic was successfully integrated into a Web-based platform to tailor evidence-based strategies to an individual's unique caregiving context and needs. Health systems are in an ideal position to adopt online technologies that provide education, skills training, and support for family caregivers of persons living with dementia.
Keywords: REACH II; caregiver burden; caregiving support; cognitive impairment; digital technology; evidence‐based programs; online platform; skills training.
© 2025 The Author(s). Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. Author disclosures are available in the Supporting Information.
Figures

References
-
- Hamel L, Montero A, The affordability of long‐term care and support services: findings from a KFF survey. KFF; 2023. November 14, 2023. Accessed September 16, 2024. https://www.kff.org/health‐costs/poll‐finding/the‐affordability‐of‐long‐...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

