Effects of Prolonged Antibiotic Therapy in Lung Abscesses-Analysis of Case Series
- PMID: 41089459
- PMCID: PMC12517991
- DOI: 10.1155/crpu/5976252
Effects of Prolonged Antibiotic Therapy in Lung Abscesses-Analysis of Case Series
Abstract
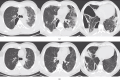
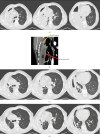
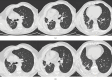
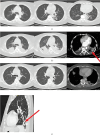
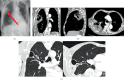
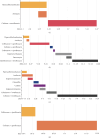
The incidence and mortality rate of lung abscess cases have declined significantly following the widespread introduction of broad-spectrum antibiotic therapy. Administration of antibiotics is considered the main treatment option, replacing invasive management, which currently is reserved only for selected patients. Four cases of patients with large lung abscesses analyzed in the article demonstrate the effectiveness of prolonged antibiotic therapy in the form of clinical improvement and regression of lesions imaged with computed tomography (CT) scans, in the absence of surgical drainage. However, the lack of a comparator group undergoing surgical interventions limits the ability to generalize the findings. The article highlights multiple diagnostic and management challenges clinicians face when treating complicated lung abscesses; however, the presented evidence is limited by a small sample size and lack of controls. Although the incidence of lung abscesses has dropped, they are still frequently seen in pulmonology, surgery, pediatrics, and internal medicine departments. In the face of the worldwide antimicrobial resistance crisis, the choice of effective antibiotic therapy remains a challenge, and there is no consensus on the duration of the treatment, as well as specific timing for introducing surgical intervention. As there are no high-quality recommendations or international studies evaluating the epidemiology of lung abscesses in the 21st century, further research seems necessary to help clinicians make appropriate therapeutic decisions.
Keywords: CT lesions; antibiotic therapy; lung abscess; lung infection; necrotic; pneumonia; resistance.
Copyright © 2025 Agata Anna Lewandowska et al. Case Reports in Pulmonology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Sabbula B. R., Rammohan G., Athavale A., Akella J. Lung Abscess . StatPearls Publishing; 2024. - PubMed
-
- Kamangar N. Lung Abscess . Medscape;
-
- Deloff L. Choroby Układu Oddechowego Pod Redakcją Prof. Leonarda Deloffa . Państwowy Zakład Wydawnictw Lekarskich; 1971.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

