Beyond anticholinergic effects: A case of trihexyphenidyl-induced bradycardia
- PMID: 41089938
- PMCID: PMC12517587
- DOI: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_113_25
Beyond anticholinergic effects: A case of trihexyphenidyl-induced bradycardia
Abstract
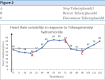
Anticholinergic drugs are extensively employed in clinical settings, with their side effects well-documented. However, paradoxical bradycardia due to trihexyphenidyl hydrochloride, an anticholinergic agent, is an infrequent and underreported phenomenon. This may be attributed to a lack of vigilant monitoring in patients undergoing therapy. Here, we present the case of a 12-year-old girl who developed sinus bradycardia following the administration of trihexyphenidyl. The heart rate normalized upon drug discontinuation. This report emphasizes the need for thorough cardiac monitoring, including baseline heart rate, Electrocardiogram (ECG), and electrolyte evaluation, before initiating therapy to prevent adverse outcomes.
Keywords: Adverse drug reaction; paradoxical bradycardia; trihexyphenidyl hydrochloride.
Copyright: © 2025 Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Blumensohn R, Razoni G, Shalev A, Munitz H. Bradycardia due to trihexyphenidyl hydrochloride. Drug Intell Clin Pharm. 1986;20:786–7. - PubMed
-
- Naranjo CA, Busto U, Sellers EM, Sandor P, Ruiz I, Roberts EA, et al. A method for estimating the probability of adverse drug reactions. Clin Pharacol Ther. 1981;30:239–45. - PubMed
-
- Kumar Panda P, Moirangthem V, Tomar A, Neyaz O, Sharawat IK. Efficacy of oral trihexyphenidyl plus clonazepam versus trihexyphenidyl for the treatment of dystonia in children with dystonic cerebral palsy: An open-label randomized controlled trial. Pediatr Neurol. 2024;158:35–40. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources