Dual Targeting of Smoothened, a Key Regulator in the Hedgehog Pathway, and BCR-ABL1 Effectively Eradicates Drug-Insensitive Stem/Progenitor Cells in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
- PMID: 41090792
- PMCID: PMC12523657
- DOI: 10.3390/cells14191565
Dual Targeting of Smoothened, a Key Regulator in the Hedgehog Pathway, and BCR-ABL1 Effectively Eradicates Drug-Insensitive Stem/Progenitor Cells in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
Abstract
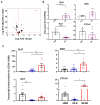
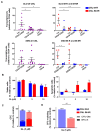
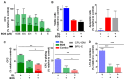
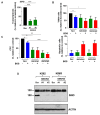
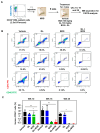
Overcoming drug resistance and targeting cancer stem cells remain challenges for curative cancer treatment. In particular, patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) often require lifelong therapy with ABL1 tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), partly due to a persistent population of TKI-resistant leukemic stem cells (LSCs). Therefore, identifying specific pathways crucial for LSC maintenance is necessary. The Hedgehog (HH) pathway, especially the protein Smoothened (SMO), has been found to be essential for CML LSCs, but its role in TKI resistance is still largely unknown. We have now demonstrated that the expression of HH pathway genes SMO and GLI2 is increased in CD34+ CML stem/progenitor cells compared to healthy counterparts, and is higher in TKI-nonresponders than in responders by transcriptome profiling and qRT-PCR analysis. Interestingly, they are most highly expressed in LSCs compared to progenitors and mature cells in TKI-nonresponders. Inhibition of SMO through genetic knockdown or with a potent, selective SMO inhibitor, Glasdegib, reduces the survival of cells from nonresponder patients. Notably, SMO inhibition also sensitizes TKI-nonresponder stem/progenitor cells to Bostutinib, a second-generation TKI, both in vitro and in a patient-derived xenotransplantation (PDX) model. These findings present a promising therapeutic target and a model for curative combination therapies in stem-cell-driven cancers.
Keywords: Bostutinib; Glasdegib (PF-04449913); Hedgehog pathway; Smoothened; chronic myeloid leukemia; leukemic stem cells; therapy-resistance; tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- Baccarani M., Deininger M.W., Rosti G., Hochhaus A., Soverini S., Apperley J.F., Cervantes F., Clark R.E., Cortes J.E., Guilhot F., et al. European LeukemiaNet recommendations for the management of chronic myeloid leukemia: 2013. Blood. 2013;122:872–884. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-05-501569. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Druker B.J., Guilhot F., O'Brien S.G., Gathmann I., Kantarjian H., Gattermann N., Deininger M.W., Silver R.T., Goldman J.M., Stone R.M., et al. Five-year follow-up of patients receiving imatinib for chronic myeloid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006;355:2408–2417. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa062867. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

