Evaluation of Nanodiamond-in-Oil Emulsion with Snake Venom to Enhance Potent Antibody Induction in Mice and Rabbits
- PMID: 41090862
- PMCID: PMC12525691
- DOI: 10.3390/nano15191518
Evaluation of Nanodiamond-in-Oil Emulsion with Snake Venom to Enhance Potent Antibody Induction in Mice and Rabbits
Abstract
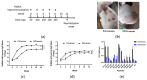
Nanodiamonds (NDs) are an innovative material in biomedical applications based on their excellent biocompatibility, nanoscale dimensions, and high surface area. In this study, we evaluated the potential of ND-in-oil emulsion to induce potent antibody responses in animals immunized with cobra venom. NDs demonstrated the capacity to bind complex venom proteins as stable conjugates, well dispersed in aqueous solution. Immunization of mice with cobra venom incorporated with ND-in-oil emulsion adjuvant (ND/venom) elicited strong venom-specific antibody responses with titers comparable to those induced by venom formulation with conventional Freund's adjuvants (FA/venom). IgG subclass analysis revealed that ND- and FA-based formulations induced a Th2-biased immune response in mice. Moreover, antibodies elicited by ND/venom or FA/venom immunization specifically recognized the epitopes of the lethal component of short-chain neurotoxin and conferred full protection against lethal cobra venom challenge (3LD50). Further, ND/venom hyperimmunization was capable of inducing high levels of neutralizing antibodies in larger animals, rabbits, highlighting the potential for antivenom manufacturing. Notably, there were no obvious lesions at the injection sites of animals that received ND/venom, in contrast to those that received FA/venom. These findings indicated NDs as an effective and safe additive in venom formulation for antivenom production.
Keywords: antivenom; cobra venom; lesion effect; nanodiamond-in-oil formulation; nanodiamonds.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors Long-Jyun Su, Hsin-Hung Lin, and Liang-Yu Chen are employed by the company LuminX Biotech Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Kasturiratne A., Wickremasinghe A.R., de Silva N., Gunawardena N.K., Pathmeswaran A., Premaratna R., Savioli L., Lalloo D.G., de Silva H.J. The global burden of snakebite: A literature analysis and modelling based on regional estimates of envenoming and deaths. PLoS Med. 2008;5:e218. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0050218. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

