Clinical Spectrum, Pathology, and Mechanisms of Anti-LGI4 Antibody-Positive Autoimmune Nodopathy
- PMID: 41092257
- PMCID: PMC12552057
- DOI: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000200504
Clinical Spectrum, Pathology, and Mechanisms of Anti-LGI4 Antibody-Positive Autoimmune Nodopathy
Abstract
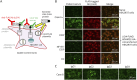
Background and objectives: The aim of this study was to elucidate the clinical spectrum and mechanisms of autoimmune nodopathy (AN) with autoantibodies against leucine-rich repeat leucin-rich glioma inactivated 1 (LGI) family member 4 (LGI4) localized at juxtaparanodes and satellite glia in the dorsal root ganglion.
Methods: We developed a live cell-based assay for LGI4-immunoglobulin (Ig) G and surveyed 131 patients with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. LGI4-IgG, anti-LGI4 antibody-negative CIDP-IgG, or healthy control (HC)-IgG were applied to Schwann cells, and cell proliferation was assayed using 5-bromo-2'-deoxyuridine labeling. Quantitative real-time PCR was used to assess the expression of Krox20 and Prx, both of which independently control peripheral nerve myelination. LGI4-IgG or HC-IgG was intraneurally injected into mouse sciatic nerves, and the effects were immunohistochemically and morphometrically assessed.
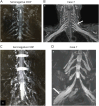
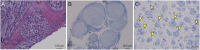
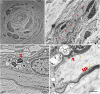
Results: Eight anti-LGI4 antibody-positive (LGI4+) patients were identified; dominant tissue-binding IgG subclasses were IgG4 in 4 patients and IgG2 and IgG3 in 2 patients each. Patients had a relatively old onset age (median 72 years, range 41-90 years). Four patients had acute/subacute monophasic courses, and 4 had chronic progressive/relapsing courses. Predominant symptoms/signs were motor weakness (8 cases), muscle atrophy (4), deep and superficial sensory impairment (8 and 7, respectively), Romberg sign (4), and hand/finger tremor (5). CSF showed extremely high protein levels (median 253 mg/dL). Three chronic cases had nerve hypertrophy. IVIg and efgartigimod were partially (7/7 patients) and markedly (1/1 patient) effective, respectively. Notably, 1 chronic patient with predominant tissue-binding LGI4-IgG2 but without LGI4-IgG4 showed a moderate reduction in myelinated fibers with endoneurial edema, numerous onion bulbs, and few inflammatory cell infiltrates in the biopsied sural nerve. Electron microscopy demonstrated onion bulb formations around the axons and subtle detachment of myelin terminal loops from axonal membranes in the paranodes. In Schwann cell culture, proliferation was significantly higher, and Krox20 but not Prx mRNA levels were lower after incubation with LGI4-IgG from chronic (but not acute-onset) cases compared with HC-IgG incubation. With intraneural injection, both LGI4-IgG4 and LGI4-IgG2 deposited mainly at the nodes extending toward the paranodes and caused nodal/paranodal alterations.
Discussion: LGI4+ AN manifests as acute/subacute monophasic and chronic progressive/relapsing diseases, sometimes exhibiting nerve hypertrophy with onion bulbs through nonmyelinating Schwann cell proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
X. Zhang reports grants from JSPS KAKENHI (Grant Nos. JP21K15703 and JP23K14783). J-I. Kira reports grants from the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED), Japan (Grant Nos. 21ek0109547h0001, 22ek0109547h0002, 23ek0109547h0003, and 23ek0109626h0001); a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (B) (JSPS KAKENHI Grant No. 22H02985); a Grant-in-Aid for Challenging Research (Exploratory) (JSPS KAKENHI Grant No. 23K18266) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, Japan; research funds from Sumitomo Pharma, Daiichi Sankyo, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, and Yamasa Corporation; and consultancy fees, speaking fees, and/or honoraria from Novartis Pharma, Argenx, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Biogen Japan, the Takeda Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Ono Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Daiichi Sankyo Co. Ltd., Alexion Pharma, Teijin Healthcare Co. Ltd., Chugai-Igakusha, Amgen Inc., Nippon-Rinsho, Hebei Medical University, and Fudan University. A. Sakoda reports a grant from JSPS KAKENHI (Grant No. JP23K14761). K-I. Yamashita reports a grant from JSPS KAKENHI (Grant No. JP20K07888). H. Ogata reports research funds from Yamasa Corporation and consultancy fees, speaking fees, and/or honoraria from CSL Behring, the Takeda Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Alnylam Pharmaceuticals Inc., Teijin Healthcare Co. Ltd., and Japan Blood Products Organization. NI reports grants from JSPS KAKENHI (Grant No. JP21K07464), AMED Japan (Grant No. 23zf0127004h0003), the Health and Labour Sciences Research Grant on Intractable Diseases (Neuroimmunological Diseases) from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan (23FC1009), Sumitomo Pharma, Daiichi Sankyo Co. Ltd., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Novartis Pharma, Biogen Japan, Yamasa Corporation, Kyowa Kirin Co., Ltd., and Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co., Ltd. and honoraria from Alexion Pharma, Novartis Pharma, Argenx, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Biogen Japan, the Takeda Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., UCB Japan, Ono Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Daiichi Sankyo Co. Ltd., Teijin Healthcare Co. Ltd., Amgen Inc., and Eisai Co. Ltd. T. Kanda reports a grant from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science; a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (A) (JSPS KAKENHI Grant No. 20H00529); and consultancy fees, speaking fees, and/or honoraria from Eisai Co. Ltd., Japan Blood Products Organization, CSL Behring, Biogen Japan, AbbVie GK, Argenx, Novartis Pharma, Tsumura, the Takeda Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Sumitomo Pharma Co. Ltd., Kyowa Kirin Co. Ltd., Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Nihon Medi-Physics Co. Ltd., Chugai-Igakusha, Nankodo, Japan Medical Journal, and Igaku-Shoin. H. Koike reports grants from JSPS KAKENHI (Grant No. JP 23K06926), AMED Japan (Grant No. 24ek0109748h0001), the Health and Labour Sciences Research Grant on Intractable Diseases (Neuroimmunological Diseases) from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan (Grant Nos. 23FC1009, 23FC1019, 23FC1035, and 23FC2001), and CSL Behring. Y. Tsuboi has received consultancy fees or honoraria from Takeda Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Sumitomo Pharma Co. Ltd., Kyowa Kirin Co. Ltd., and Eisai Co. Ltd. M. Kobayashi has received payment for presentations from CSL Behring and Japan Blood Products Organization and for educational events from Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. K. Kitagawa has received speaking fees from Daiichi Sankyo Co. Ltd., Kowa Pharmaceutical Company, and Kyowa Kirin Co. Ltd. T. Imamura reports grant from JSPS KAKENHI (Grant No. JP 22K07499). T. Imamura reports grant from JSPS KAKENHI (Grant No. JP 22K07499) and speaking fees from Tsumura & Co. and Kowa Company Ltd. G. Maimaitijiang reports a grant from JSPS KAKENHI (Grant No. JP 22K15717). Y. Nakamura reports a grant from JSPS KAKENHI (Grant No. JP 21K07467) and speaking fees and/or honoraria from Novartis Pharma, Biogen Japan, the Takeda Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., and Chugai-Igakusha. A. Yokote, M. Mitsuishi, T. Tashiro, R. Sato, T. Ide, T. Mishima, Y. Namihira, Y. Ohya, Y. Fukata, and M. Fukata report nothing to declare. Go to
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
