Microglia-specific regulation of lipid metabolism in Alzheimer's disease revealed by microglial depletion in 5xFAD Mice
- PMID: 41093842
- PMCID: PMC12528747
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-64161-z
Microglia-specific regulation of lipid metabolism in Alzheimer's disease revealed by microglial depletion in 5xFAD Mice
Abstract
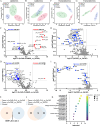
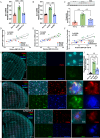
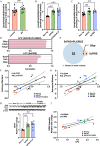
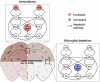
Abnormal lipid metabolism is observed in Alzheimer's disease (AD), but its contribution to disease progression remains unclear. Genetic studies indicate that microglia, the brain's resident immune cells, influence lipid processing during AD. Here, we show that microglia-the brain's resident immune cells-selectively regulate lipid accumulation that associated with disease pathology in both AD mouse models and human postmortem brains. Using lipidomics and histological analysis, we identify a striking buildup of arachidonic acid-containing bis(monoacylglycero)phosphate in response to amyloid plaques, which depends on microglial activity and the AD risk gene GRN. In contrast, lysophosphatidylcholine and lysophosphatidylethanolamine accumulate independently of microglia, correlating instead with astrocyte activation and oxidative stress. These results connect dysregulated lipid metabolism in AD to distinct brain cell types and molecular pathways. Our findings highlight microglial lipid homeostasis as a potential therapeutic target for modifying disease progression in AD.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Winblad, B. et al. Defeating Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias: a priority for European science and society. Lancet Neurol.15, 455–532 (2016). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- AG085545/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Aging (U.S. National Institute on Aging)
- AG061872/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Aging (U.S. National Institute on Aging)
- AG061729/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Aging (U.S. National Institute on Aging)
- AG066546/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Aging (U.S. National Institute on Aging)
- AG013319/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Aging (U.S. National Institute on Aging)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

