Budigalimab, an anti-PD-1 inhibitor, for people living with HIV-1: a randomized, placebo-controlled phase 1b study
- PMID: 41094034
- PMCID: PMC12618229
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-025-03993-0
Budigalimab, an anti-PD-1 inhibitor, for people living with HIV-1: a randomized, placebo-controlled phase 1b study
Abstract
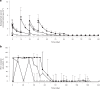
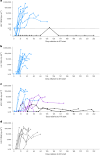
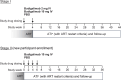
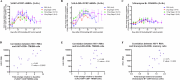
Chronic human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) disease results in immune exhaustion and dampened T cell responses, and programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) inhibitors offer a potential approach to enable viral control without antiretroviral therapy (ART) through reversal of these effects. Budigalimab is an investigational humanized anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody. Multiple intravenous (IV) low doses of budigalimab (Stage 1: 2 mg n = 10, 10 mg n = 10, placebo n = 5, two doses every 4 weeks; Stage 2: 10 mg n = 11, placebo n = 5, four doses every 2 weeks (Q2W)) were assessed in people living with HIV (PLWH; n = 41) in a randomized, double-blind, multicenter, placebo-controlled phase 1 study with an analytical treatment interruption (ATI) to identify an efficacious regimen with a favorable safety profile in PLWH. The primary endpoints were safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetics. Demographics and baseline characteristics were balanced across treatment groups, except for sex, which was mostly male. All participants identified as cisgender. Budigalimab was well tolerated for up to 44 weeks, with 29 of 41 participants experiencing an adverse event (AE), including 2 participants who each experienced one grade 1 reversible immune-related AE (thyroiditis, hyperthyroidism). Three grade 3 AEs were reported by two participants and one serious AE by one participant; none were deemed related to treatment. IV budigalimab 10 mg Q2W resulted in a slight accumulation of drug in serum, with concentrations remaining above the estimated concentration required for near-complete (>95%) PD-1 receptor saturation on CD8+ T cells for ~10 weeks in peripheral blood. In an exploratory efficacy analysis of a 12-week ATI initiated with the first of four 10 mg Q2W doses, 6 of 11 participants experienced a delayed rebound with a relatively low viral peak and/or off-ART viral control (<200 copies ml-1) for ≥6 weeks during ATI, with 2 sustaining ART-free viral control to study end (204-252 days). The study achieved prespecified endpoints, supporting further evaluation of budigalimab in PLWH in a phase 2 study. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT04223804 .
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: M.N.R. is a speaker for AbbVie, Gilead Sciences and ViiV Healthcare and is a consultant for Gilead Sciences, ViiV Healthcare, Merck and Abbott. J.P.L. has no disclosures to declare. A.G.P.d.S., P.K., T.R.V., F.Z., H.B., P.D. and N.M.M. are employees of AbbVie and may own stock and/or stock options. M.L.A. sits on the Gilead Sciences advisory board. F.F. is a speaker and consultant for AbbVie, Gilead Sciences, Merck & Co. and ViiV Healthcare. J.P.R. is a speaker and consultant for AbbVie, Gilead Sciences, Merck & Co., Moderna and ViiV Healthcare and is partially supported for research infrastructure from the Canadian HIV cure entreprise 3.0 (CIHR: BR4-197730).
Figures


References
-
- AIDSinfo. Global HIV & AIDS statistics (United Nations Joint Programme on HIV/AIDS). http://aidsinfo.unaids.org (accessed 19 August 2024).
-
- Peterson, T. E. & Baker, J. V. Assessing inflammation and its role in comorbidities among persons living with HIV. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis.32, 8–15 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Hasse, B. et al. Morbidity and aging in HIV-infected persons: the Swiss HIV cohort study. Clin. Infect. Dis.53, 1130–1139 (2011). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

