A human YEATS4 variant confers resistance to TST and IGRA conversion despite Mycobacterium tuberculosis exposure
- PMID: 41094526
- PMCID: PMC12522460
- DOI: 10.1186/s13073-025-01547-0
A human YEATS4 variant confers resistance to TST and IGRA conversion despite Mycobacterium tuberculosis exposure
Abstract
Background: Despite sustained exposure to Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb), some individuals-so-called resisters-have persistently negative results for the tuberculin skin test (TST) and interferon-gamma release assays (IGRAs). "Resistance to immune conversion" is the best-known clinical correlate for absence of Mtb transmission and protection from tuberculosis (TB). We investigated the human genetic basis of this phenotype by hypothesizing that resisters living with HIV, a major risk factor for TB, would be enriched in genotypes conferring resistance.
Methods: We enrolled two cohorts of people living with HIV (PWH), consisting of 55 resisters and 100 controls-either positive for TST and IGRA or with a history of TB-from South Africa, and 66 resisters and 57 controls from Haiti, two regions where TB is hyperendemic. All study participants underwent whole-genome sequencing (WGS). We performed a genome-wide association study (GWAS) of the resister phenotype, focusing on a comprehensive set of 320,629 common protein-altering and regulatory variants.
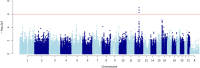
Results: We identified a cluster of variants on chromosome 12q15, including rs622656, associated with the resister phenotype in both South Africa and Haiti. A meta-analysis revealed that the C allele of rs622656 was associated with the resister phenotype with an odds ratio (OR) of 4.35 (95% CI: 2.44-7.69) (P = 2.47 × 10-7). The frequency of the C allele in the combined sample was 0.11, and all four CC homozygotes in our sample were resisters. Consistently, we found a significant depletion of homozygous carriers of the rs622656-C resistance-associated allele in three cohorts of HIV-negative TB patients from Haiti, Morocco, and the UK Biobank. In silico analysis suggested that the rs622656-C resistance-associated allele increased the translation of the nearby YEATS4 gene by suppressing an upstream open reading frame. YEATS4 has been shown to play a role in innate lymphoid cell differentiation, a leukocyte subset. We confirmed experimentally that the rs622656-C resistance-associated allele increased the activity of the reporter gene in HEK293T cells.
Conclusions: We report a new cluster of variants on chromosome 12q15, overlapping the YEATS4 gene, strongly associated with the resister phenotype in two populations of PWH. Our results contribute to the understanding of the molecular mechanisms that block transmission of Mtb.
Keywords: Mycobacterium tuberculosis; YEATS4; Genome-wide association study; Human immunodeficiency virus; IGRA; Regulatory variants; Resister; TST; Whole genome sequencing.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The Cape Town study was approved by the Health Research Ethics Committee (HREC) of Stellenbosch University [N16/03/033 and N16/03/033A] and the Faculty of Health Sciences Human Research Ethics Committee of the University of Cape Town [HREC 755/2016 and 702/2017]. Approval was also obtained for access to the relevant clinics from the City of Cape Town and Western Cape government. All the participants enrolled provided written informed consent for participation and were recruited through protocols approved by the competent local ethics committees. All research was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2024. 2024.
-
- World Health Organization. Global tuberculosis report 2020. 2020.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

