Spatial Transcriptomics of Adipose Tissue: Technologies, Applications, and Challenges
- PMID: 41094746
- PMCID: PMC12583788
- DOI: 10.7570/jomes25078
Spatial Transcriptomics of Adipose Tissue: Technologies, Applications, and Challenges
Abstract
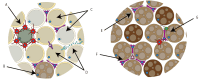
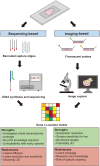
Adipose tissue is a complex metabolic and endocrine organ that plays a central role in systemic energy homeostasis. While single-cell and single-nucleus RNA sequencing have revealed remarkable cellular heterogeneity within adipose tissue depots, these approaches lack spatial context, limiting the ability to understand how cellular organization and microenvironmental cues shape adipose tissue biology. Spatial transcriptomics (ST) has emerged as a powerful technology to overcome this barrier by allowing one to map gene expression directly within intact tissue sections. Recent advances in ST platforms now permit analysis at a high resolution, enabling interrogation of adipocyte subpopulations, stromal progenitors, immune cell infiltration, and tissue remodeling. In this review, we provide an overview of current ST technologies, computational strategies for analysis, and recent applications for understanding adipose tissue biology. We further highlight key opportunities for ST to address unanswered questions surrounding adipogenic niches, depot-specific remodeling, and immune cell interactions. Together, these advances position ST as a transformative tool for dissecting the architecture and function of adipose tissue in health and metabolic disease.
Keywords: Adipose tissue; Cell plasticity; Gene expression profiling; Spatial analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
James G. Granneman is an editorial board member of the journal. But he was not involved in the peer reviewer selection, evaluation, or decision process of this article. No other potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

