Adaptive Antenna for Maritime LoRaWAN: A Systematic Review on Performance, Energy Efficiency, and Environmental Resilience
- PMID: 41094933
- PMCID: PMC12526727
- DOI: 10.3390/s25196110
Adaptive Antenna for Maritime LoRaWAN: A Systematic Review on Performance, Energy Efficiency, and Environmental Resilience
Abstract
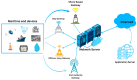
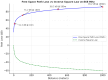
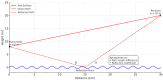
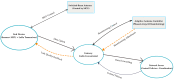
Long Range Wide Area Network (LoRaWAN) has become an attractive option for maritime communication because it is low-cost, long-range, and energy-efficient. Yet its performance at sea is often limited by fading, interference, and the strict energy budgets of maritime Internet of Things (IoT) devices. This review, prepared in line with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) 2020 guidelines, examines 23 peer-reviewed studies published between 2019 and 2025 that explore adaptive antenna solutions for LoRaWAN in marine environments. The work covered four main categories: switched-beam, phased array, reconfigurable, and Artificial Intelligence or Machine Learning (AI/ML)-enabled antennas. Results across studies show that adaptive approaches improve gain, beam agility, and signal reliability even under unstable conditions. Switched-beam antennas dominate the literature (45%), followed by phased arrays (30%), reconfigurable designs (20%), and AI/ML-enabled systems (5%). Unlike previous reviews, this study emphasizes maritime propagation, environmental resilience, and energy use. Despite encouraging results in signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), packet delivery, and coverage range, clear gaps remain in protocol-level integration, lightweight AI for constrained nodes, and large-scale trials at sea. Research on reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RIS) in maritime environments remains limited. However, these technologies could play an important role in enhancing spectral efficiency, coverage, and the scalability of maritime IoT networks.
Keywords: IoT; LoRaWAN; SNR; adaptive antennas; beamforming; energy efficiency; maritime environment; systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Dinis H., Rocha J., Matos T., Gonçalves L.M., Martins M. The Challenge of Long-Distance Over-the-Air Wireless Links in the Ocean: A Survey on Water-to-Water and Water-to-Land MIoT Communication. Appl. Sci. 2022;12:6439. doi: 10.3390/app12136439. - DOI
-
- Patriti T., Mirri S., Girau R. A LoRa-Mesh Based System for Marine Social IoT; Proceedings of the IEEE Consumer Communications and Networking Conference (CCNC); Las Vegas, NV, USA. 8–11 January 2023; pp. 329–332. - DOI
-
- Habib A., Moh S. Wireless Channel Models for Over-the-Sea Communication: A Comparative Study. Appl. Sci. 2019;9:443. doi: 10.3390/app9030443. - DOI
-
- Pal A., Rahman R. Communication for Underwater Sensor Networks: A Comprehensive Summary; Association for Computing Machinery, New York, United States. ACM Trans. Sens. Netw. 2022;19:22. doi: 10.1145/3546827. - DOI
-
- Alexiou A., Haardt M. Smart Antenna Technologies for Future Systems: Trends and Challenges. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2004;42:90–97. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2004.1336725. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

