Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Botulinum Therapy Based on the Anthropometric Characteristics of the Face Using Non-Invasive Thermal Imaging Data
- PMID: 41095738
- PMCID: PMC12524183
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics15192519
Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Botulinum Therapy Based on the Anthropometric Characteristics of the Face Using Non-Invasive Thermal Imaging Data
Abstract
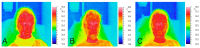
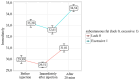
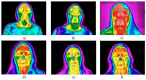
Objective: The objective of this study was to clarify the connection between BTX-A injections and local changes in skin temperature and to assess the correlation between post-BTX-A injection facial vascular hyperthermia and subcutaneous adipose tissue thickness (SAT) in the frontal area using thermography. Methods: The study involved 30 patients (mean age 42 ± 0.5 years; 18 women, 12 men). Facial skin temperature was measured via thermography (Thermo GEAR G30) before, immediately after, and 20 min after subcutaneous injection of BTX-A with hemagglutinin complex, gelatin (6 mg), and maltose monohydrate (12 mg). SAT development was graded by combined visual-palpation assessment. Statistical analysis included Student's t-test and the Mann-Whitney U-test. Results: Biphasic thermal response: immediately post-injection: Significant decrease in min (-1.1 °C) and mean (-0.3 °C) facial temperatures (p < 0.05); 20 min post-injection: pronounced increase in mean (+1.5 °C), max (+1.3 °C), and min (+1.6 °C) temperatures (p < 0.001), attributed to BTX-A-induced vasodilation and local inflammation. Subjects with pronounced SAT exhibited significantly higher baseline temperatures (Me = 33.1 °C vs. 29.8 °C; p < 0.001) and more intense hyperthermic responses (+1.6 °C mean increase vs. +1.1 °C in low-SAT group; p < 0.001). Pronounced SAT was predominantly female (10/15; p < 0.05) and linked to higher BMI (33.3% overweight vs. 0% in low-SAT; *p = 0.036*). Conclusions: SAT thickness is a key determinant of post-BTX-A vascular hyperthermia, with pronounced SAT predicting stronger reactions. Practical Recommendation: Targeted local hypothermia (+4 °C to +8 °C for 5-7 min post-injection, adjustable by SAT thickness) mitigates hyperemia, edema, hematoma risk, and potential toxin diffusion, especially in high-SAT individuals.
Keywords: botulinum neuroprotein; injections; subcutaneous fat tissue; thermography.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Whitmer A.M. A Mixed Course-Based Research Approach to Human Physiology. Iowa State University Digital Press; Ames, IA, USA: 2021. [(accessed on 1 August 2025)]. Available online: https://iastate.pressbooks.pub/curehumanphysiology/
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

