Clinical Outcomes of Cardiac Implantable Electronic Device-Related Endocarditis: An International ID-IRI Study
- PMID: 41095899
- PMCID: PMC12525113
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14196816
Clinical Outcomes of Cardiac Implantable Electronic Device-Related Endocarditis: An International ID-IRI Study
Abstract
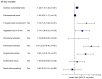
Background/Objectives: Cardiac implantable electronic device-related infective endocarditis (CIED-RIE) is a serious condition with significant morbidity and mortality. Although recent advances in imaging and therapeutic approaches have improved management, diagnosing and treating CIED-RIE continues to be challenging. This study aimed to identify factors associated with mortality in CIED-RIE patients. Methods: We conducted a retrospective, multicenter international study of adult patients diagnosed with CIED-RIE between January 2014 and June 2024. Data on demographics, clinical presentation, microbiological findings, imaging results, treatment modalities, and outcomes were collected and analyzed to determine predictors of short-term mortality. Results: A total of 197 patients (mean age: 65.3 ± 14.4 years; 75.1% male) were included. The most common device type was permanent pacemaker (48.2%). Staphylococcus species were the predominant pathogens (62.4%). Surgical intervention was performed in 67.5% of patients, and 90-day mortality occurred in 19.3%. Multivariable analysis identified higher Charlson comorbidity index (HR: 1.31), tricuspid valve involvement (HR: 2.35), vegetation size ≥ 10 mm (HR: 2.53), pulmonary embolism (HR: 3.92), and absence of surgical intervention (HR: 2.90) as independent predictors of increased 90-day mortality. Conclusions: Early identification of high-risk patients and prompt multidisciplinary management, including surgical intervention when indicated, are critical to improving outcomes in patients with CIED-RIE.
Keywords: cardiac implantable electronic device; clinical outcome; endocarditis; mortality; transvenous lead extraction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Blomströ M-Lundqvist C., Traykov V., Erba P.A., Burri H., Nielsen J.C., Bongiorni M.G., Poole J., Boriani G., Costa R., Deharo J.-C., et al. European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) international consensus document on how to prevent, diagnose, and treat cardiac implantable electronic device infections-endorsed of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID) in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS) Europace. 2020;22:515–516. doi: 10.1093/europace/euz246. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fowler V.G., Durack D.T., Selton-Suty C., Athan E., Bayer A.S., Chamis A.L., Dahl A., DiBernardo L., Durante-Mangoni E., Duval X., et al. The 2023 Duke-International Society for Cardiovascular Infectious Diseases Criteria for Infective Endocarditis: Updating the Modified Duke Criteria. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2023;77:518–526. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciad271. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

