The Impact of COVID-19 on Long-Term Mortality in Maintenance Hemodialysis: 5 Years Retrospective Cohort Study
- PMID: 41096159
- PMCID: PMC12524824
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14197081
The Impact of COVID-19 on Long-Term Mortality in Maintenance Hemodialysis: 5 Years Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
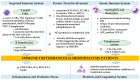
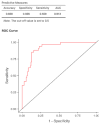
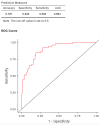
Background: Hemodialysis (HD) patients are a highly vulnerable population with elevated mortality driven by comorbidities and dialysis-specific factors. While most studies focused on intra-pandemic outcomes, long-term effects remain underexplored. We aimed to evaluate 5-year mortality and the impact of COVID-19 vaccination in chronic HD patients. Methods: A retrospective study was conducted on 211 HD patients monitored between 2020 and 2024. Outcomes included overall and cardiovascular mortality, risk factors in COVID-19-positive patients, and vaccination impact. Logistic regression identified independent predictors. Results: The cohort had a mean age of 65.6 ± 13.3 years, with 55.9% males and mean dialysis vintage of 6.9 ± 5.5 years. Overall mortality reached 53.6%, while 38.4% were vaccinated. Predictors of all-cause mortality included age (OR = 1.078, p < 0.001), BMI (OR = 0.868, p < 0.001), hemoglobin (OR = 0.581, p < 0.001), phosphorus (OR = 1.351, p = 0.025), dialysis adequacy (OR = 0.138, p = 0.013), and ischemic cardiopathy (OR = 0.327, p = 0.009). In COVID-19-positive patients, mortality was associated with age (OR = 1.069, p = 0.002), low hemoglobin (OR = 0.642, p = 0.014), BMI (OR = 0.885, p = 0.009), CRP (OR = 1.015, p < 0.001), and coronary artery disease (OR = 5.68, p < 0.001). Cardiovascular disease was the leading cause of death (44.6% in COVID-19-positive vs. 73.3% in negatives, p = 0.006). Vaccination significantly reduced COVID-19-related mortality (OR = 0.023, p = 0.005) but did not influence overall or non-COVID mortality. Conclusions: Five-year mortality in HD patients remained high, mainly cardiovascular, and was strongly influenced by age, BMI, hemoglobin, dialysis adequacy, and comorbidities. COVID-19 vaccination substantially reduced COVID-related mortality but did not alter all-cause outcomes. These findings support vaccination and careful risk stratification in HD populations for future pandemics.
Keywords: COVID-19 infection; anti-SARS-CoV2 vaccination; cardiac mortality; hemodialysis; mortality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Francis A., Harhay M.N., Ong A.C.M., Tummalapalli S.L., Ortiz A., Fogo A.B., Fliser D., Roy-Chaudhury P., Fontana M., Nangaku M., et al. Chronic kidney disease and the global public health agenda: An international consensus. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2024;20:473–485. doi: 10.1038/s41581-024-00820-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Foreman K.J., Marquez N., Dolgert A., Fukutaki K., Fullman N., McGaughey M., Pletcher M.A., Smith A.E., Tang K., Yuan C.W., et al. Forecasting life expectancy, years of life lost, and all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 250 causes of death: Reference and alternative scenarios for 2016-40 for 195 countries and territories. Lancet. 2018;392:2052–2090. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31694-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- ERA Registry Annual Report. [(accessed on 23 July 2024)]. Available online: https://www.era-online.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/09/ERA-Registry-Annua....
-
- Ratiu I.A., Moisa C.F., Țiburcă L., Hagi-Islai E., Ratiu A., Bako G.C., Ratiu C.A., Stefan L. Antimicrobial Treatment Challenges in the Management of Infective Spondylodiscitis Associated with Hemodialysis: A Comprehensive Review of Literature and Case Series Analysis. Antibiotics. 2024;13:284. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13030284. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ratiu I.A., Mihaescu A., Olariu N., Ratiu C.A., Bako C.G., Ratiu A., Indries M., Fratila S., Dejeu D., Teusdea A., et al. Hepatitis C Virus Infection in Hemodialysis Patients in the Era of Direct-Acting Antiviral Treatment: Observational Study and Narrative Review. Medicina. 2024;60:2093. doi: 10.3390/medicina60122093. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

