Co-Stimulatory and Immune Checkpoint Molecule Expression on Peripheral Immune Cells Differs Age Dependently Between Healthy Donors and Patients with Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 41097741
- PMCID: PMC12523874
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers17193215
Co-Stimulatory and Immune Checkpoint Molecule Expression on Peripheral Immune Cells Differs Age Dependently Between Healthy Donors and Patients with Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
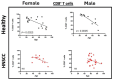
Introduction: The analysis of exhaustion marker expression, like immune checkpoint molecules (ICMs) on tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes as well as peripheral immune cells of patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC), is of high interest since it reveals information about the patient's immune status and the effectiveness of immune modulation. However, data regarding age-dependent expression are lacking. Here, we demonstrate an increase in most ICMs associated with age and disease, suggesting immune checkpoint modulation as an evidence-based option for the treatment of aged HNSCC patients.
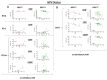
Material and methods: Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) (healthy: n = 30 with an age range from 21 to 84 years/HNSCC: n = 37 with an age range from 37 to 94 years) were analyzed via flow cytometry following (density gradient separation) standard protocol. Flow cytometry was performed using CD4 and CD8 as backbone markers as well as co-stimulatory molecules like CD137, OX40, GITR, and CD27 or ICM like PD-1, CTLA4, BTLA, LAG3, or TIM3 using a Gallios flow cytometer (Beckman Coulter, Brea, CA, USA).
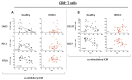
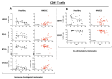
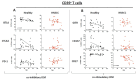
Results: We found a statistically significant decreased ICM expression on the PBMCs of healthy donors with increasing age. However, the expression of ICMs in HNSCC was significantly increased (PD1 on CD4+ T cells: p = 0.001), while we found a decreased co-stimulatory molecule expression (e.g., CD27 on CD4+ T cells and CD39+ T cells: p = 0.003 and p = 0.009, respectively). Immune cells of HPVneg HNSCC have a significant age-dependent decrease in CD27 expression on CD8+, CD4+, and CD39+ T cells (p = 0.0426, p = 0.0078, and p = 0.0078, respectively).
Conclusions: This study sheds light on the changing co-stimulatory molecule/ICM expression regarding the patient's age and reveals an increase in most immune checkpoint molecules for HNSCC patients according to their age. This new evidence is valuable in ensuring individualized therapeutic approaches in the increasingly relevant field of checkpoint inhibition, even in old age.
Keywords: HNSCC; ageing; immune checkpoints; immune senescence; targeted immunotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Simon Laban: Advisory Boards: Merck Sharp & Dohme, Bristol Myers Squibb, Astra Zeneca, Sanofi Genzyme. Honoraria: Merck Sharp & Drohme, Bristol Myers Squibb, Astra Zeneca, Merck Serono. The other authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- GBD 2016 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet. 2017;390:1211–1259. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32154-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- von Witzleben A., Currall E., Wood O., Chudley L., Akinyegun O., Thomas J., Bendjama K., Thomas G.J., Friedmann P.S., King E.V., et al. Correlation of HPV16 Gene Status and Gene Expression with Antibody Seropositivity and TIL Status in OPSCC. Front. Oncol. 2020;10:591063. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.591063. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Burtness B., Harrington K.J., Greil R., Soulieres D., Tahara M., de Castro G., Jr., Psyrri A., Baste N., Neupane P., Bratland A., et al. Pembrolizumab alone or with chemotherapy versus cetuximab with chemotherapy for recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (KEYNOTE-048): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet. 2019;394:1915–1928. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32591-7. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

