Ginsenoside Rg5 Improves Radiation-Induced Heart Injury via PPARG/PDK1/AKT1 Pathway
- PMID: 41097812
- PMCID: PMC12528005
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.70852
Ginsenoside Rg5 Improves Radiation-Induced Heart Injury via PPARG/PDK1/AKT1 Pathway
Abstract
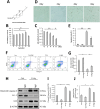
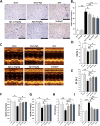
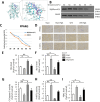
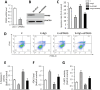
Ginsenoside Rg5 (G-Rg5), a rare extract of ginseng, has proven to be valuable for a wide range of clinical applications. However, the role of G-Rg5 in radiation-induced heart injury is currently unclear. This study aims to explore the intervention effect and possible treatment mechanism of G-Rg5 on radiation-induced heart injury. We investigated the impact of G-Rg5 on radiation-induced heart injury through in vivo and in vitro studies. Network pharmacology was employed to explore potential key targets and molecular mechanisms. Various experimental methods were utilised to validate the effects of G-Rg5 on the PPARG/PDK1/AKT1 pathway. G-Rg5 alleviated radiation-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis and cardiac functional impairment. The expression of peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma (PPARG) was upregulated following G-Rg5 treatment, thereby suppressing the transcription of phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 (PDK1), a predicted target gene regulated by PPARG, to enhance AKT serine/threonine kinase 1 (AKT1) phosphorylation levels. The protective effect of G-Rg5 against radiation-induced heart injury was found to be compromised upon inhibition or knockdown of PPARG. The interaction between PPARG and PDK1 was confirmed by the results of chromatin immunoprecipitation and luciferase reporter assays. G-Rg5, through the upregulation of PPARG expression, induces the transcription of PDK1 and subsequently enhances the phosphorylation levels of AKT1. Ultimately, this process plays a crucial role in mitigating cellular apoptosis and functional decline in radiation-induced heart injury. Therefore, G-Rg5 holds great potential as a therapeutic agent for radiation-induced heart injury.
Keywords: PPARG/PDK1/AKT1; apoptosis; ginsenoside Rg5; radiation‐induced heart disease.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Slezak J., Kura B., Babal P., et al., “Potential Markers and Metabolic Processes Involved in the Mechanism of Radiation‐Induced Heart Injury,” Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology 95, no. 10 (2017): 1190–1203. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

