Efficient FPGA implementation of polar codes-based information reconciliation for quantum key distribution
- PMID: 41102450
- PMCID: PMC12533042
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-20146-y
Efficient FPGA implementation of polar codes-based information reconciliation for quantum key distribution
Abstract
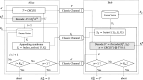
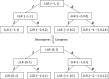
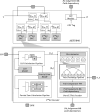
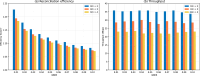
Quantum key distribution (QKD) leverages the principles of quantum mechanics to generate unconditionally secure keys for remote communication, even in the presence of an eavesdropper with unlimited computational power. A critical component of QKD is information reconciliation (IR), which corrects bit errors introduced by system imperfections and channel noise, ensuring the integrity of the shared key. Polar codes-based IR schemes have attracted considerable attention due to their near-Shannon-limit performance and low computational complexity. However, existing implementations primarily rely on CPUs or GPUs, which are suboptimal in terms of performance and energy efficiency. Here, we present a hardware accelerator designed specifically for discrete variable QKD (DV-QKD), targeting polar codes-based IR and implemented on a cost-effective FPGA platform. Our design achieves high throughput and scalability by employing a module-level pipeline parallel structure, a fully parallelized decoding strategy, and a hybrid memory architecture. This approach enhances decoder efficiency and optimizes resource utilization. On this platform, we demonstrate an IR throughput of 35.33 Mbps for a block size of [Formula: see text], providing a real-time, cost-efficient solution that significantly enhances the performance of QKD systems.
Keywords: Discrete variable quantum key distribution (DV-QKD); Field programmable gate array (FPGA); Information reconciliation (IR); Polar codes.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Scarani, V. et al. The security of practical quantum key distribution. Reviews of modern physics81(3), 1301–1350 (2009).
-
- Lo, H. K., Curty, M., & Tamaki, K. Secure quantum key distribution. Nature Photonics8(8), 595–604 (2014).
-
- Wang, W. et al. Fully Passive Quantum Key Distribution. Physical Review Letters130(22), 220801 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Lucamarini, M., Yuan, Z. L., Dynes, J. F. & Shields, A. J. Overcoming the rate–distance limit of quantum key distribution without quantum repeaters. Nature557(7705), 400–403 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Lo, H. K., Curty, M., & Qi, B. Measurement-Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution. Physical Review Letters108(13), 130503 (2012). - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

