Rbm20 antisense oligonucleotides alleviate diastolic dysfunction in a mouse model of cardiometabolic heart failure (HFpEF)
- PMID: 41104480
- PMCID: PMC12560776
- DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvaf171
Rbm20 antisense oligonucleotides alleviate diastolic dysfunction in a mouse model of cardiometabolic heart failure (HFpEF)
Abstract
Aims: Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is prevalent, deadly, and difficult to treat. Risk factors such as obesity and hypertension contribute to cardiac inflammation, metabolic defects, and pathological remodelling that impair ventricular filling in diastole. Titin based stiffness is a main determinant of diastolic function and can be adjusted by the splicing regulator RNA binding motif protein 20 (RBM20). Inhibition of RBM20 using antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) induces expression of compliant titin isoforms, which reduce stiffness. However, dose finding and documenting utility in primarily cardiometabolic disease remains challenging.
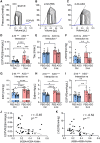
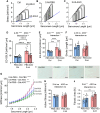
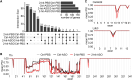
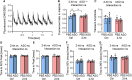
Methods and results: Here, we optimized RBM20-ASO dosing in a HFpEF mouse model that closely mimics human disease, characterized by metabolic syndrome and comorbidities, but without primary defects in titin or RBM20. Partial inhibition of RBM20 (∼50%) selectively increased compliant titin isoforms, improving diastolic function while preserving systolic performance. This intervention reduced left ventricular stiffness, enhanced relaxation, and mitigated cardiac hypertrophy, despite ongoing systemic comorbidities.
Conclusion: Our findings demonstrate that targeting titin stiffness with Rbm20-ASOs can serve as an alternative or adjunctive therapeutic strategy for HFpEF to restore cardiac function and prevent further organ damage. The approach may offer benefits even in the presence of phenotypic heterogeneity and unresolved systemic comorbidities.
Keywords: ASO; HFpEF; RBM20; Therapy; Titin.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: Dr Gotthardt has a consultancy agreement with River BioMedics. Dr Guo has a consultancy agreement with Alexion Pharmaceuticals.
Figures




References
-
- Borlaug BA. Evaluation and management of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Nat Rev Cardiol 2020;17:559–573. - PubMed
-
- Zile MR, Baicu CF, Ikonomidis JS, Stroud RE, Nietert PJ, Bradshaw AD, Slater R, Palmer BM, Van Buren P, Meyer M, Redfield MM, Bull DA, Granzier HL, LeWinter MM. Myocardial stiffness in patients with heart failure and a preserved ejection fraction: contributions of collagen and titin. Circulation 2015;131:1247–1259. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL171047/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- SFB 1470/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft
- TAN CASTT-21CVD02/Leducq Foundation
- B04/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft
- AdG 101055339/ERC
- R01HL171047/National Institute of Health
- 23TPA1069731/American Heart Association
- R35HL144998/National Institute of Health
- Z01/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft
- 19TPA3480072/American Heart Association
- R01 HL148733/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 HL144998/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL148733/National Institute of Health
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

