Multi‑omics reveal neutrophil heterogeneity in sepsis (Review)
- PMID: 41104871
- PMCID: PMC12534110
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2025.5663
Multi‑omics reveal neutrophil heterogeneity in sepsis (Review)
Abstract
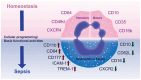
Sepsis is a life‑threatening disease characterized by a dysregulated immune response, and neutrophils serve an important role in pathogen clearance, multiple organ failure and immune regulation. With the discovery of multiple phenotypical and functional variants of neutrophils in sepsis, the heterogeneity of neutrophils is crucial, as it impacts the effectiveness of the immune response and the overall outcome of sepsis. Various genome, transcriptome, proteome and metabolome properties may contribute to this heterogeneity. Multi‑omics approaches unveil complex details of neutrophil behavior in the context of sepsis, highlighting how neutrophil phenotypes are differentially recruited and activated in response to various stimuli. The present review aimed to provide an overview of the differences in neutrophil phenotypes and functions during sepsis, focusing on neutrophil heterogeneity identified via multi‑omics methods. Comprehensive understanding of multi‑omics data regarding neutrophil heterogeneity enhances the diagnostic accuracy of sepsis and provides a scientific basis for individualized treatment strategies, potentially improving patient outcomes by targeting specific neutrophil functions and states.
Keywords: heterogeneity; multi‑omics; neutrophil; sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Rudd KE, Johnson SC, Agesa KM, Shackelford KA, Tsoi D, Kievlan DR, Colombara DV, Ikuta KS, Kissoon N, Finfer S, et al. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990-2017: Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet. 2020;395:200–211. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32989-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fleischmann C, Scherag A, Adhikari NK, Hartog CS, Tsaganos T, Schlattmann P, Angus DC, Reinhart K, International Forum of Acute Care Trialists Assessment of global incidence and mortality of hospital-treated sepsis. Current estimates and limitations. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2016;193:259–272. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201504-0781OC. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
