Palmitoyltransferase ZDHHC19 regulates histone-to-protamine exchange during spermiogenesis in mice
- PMID: 41105761
- PMCID: PMC12533564
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adv5189
Palmitoyltransferase ZDHHC19 regulates histone-to-protamine exchange during spermiogenesis in mice
Abstract
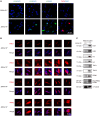
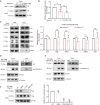
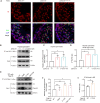
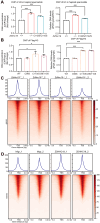
Spermiogenesis, the final phrase of spermatogenesis, involves replacing histones by protamines, a process known as histone-to-protamine exchange, which is crucial for chromatin condensation. While this exchange is essential, the precise mechanisms remain incompletely understood. In this study, we discovered that the palmitoyltransferase ZDHHC19 functions as a key regulator of mouse spermiogenesis. Loss of Zdhhc19 leads to male infertility and abnormal sperm morphology. Zdhhc19-deficient sperm exhibit impaired histone-to-protamine exchange, leading to retention of histones and misdistribution of protamines. Similarly, the palmitoyltransferase catalytic site mutant Zdhhc19 C142S knock-in mice show reduced fertility, sperm abnormalities, and histone retention. Mechanistically, ZDHHC19 mediates histone H3 palmitoylation at cysteine-110, weakening H3-H4 interactions and increasing chromatin accessibility. Palmitoylation of H3 facilitates histone-to-protamine exchange. This study highlights the essential role of ZDHHC19's palmitoyl-transferase activity in histone-to-protamine exchange during spermiogenesis and underscores the broader role of histone palmitoylation in chromatin remodeling.
Figures



References
-
- Toshimori K., Ito C., Formation and organization of the mammalian sperm head. Arch. Histol. Cytol. 66, 383–396 (2003). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

