Novel combination therapy with phenformin enhances the effects of lenvatinib in hepatocellular carcinoma via AMPK-mediated PDGFRβ degradation
- PMID: 41107802
- PMCID: PMC12534998
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-025-04012-5
Novel combination therapy with phenformin enhances the effects of lenvatinib in hepatocellular carcinoma via AMPK-mediated PDGFRβ degradation
Abstract
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is an invasive malignant tumour for which few effective treatment options are currently available. Lenvatinib is a small-molecule inhibitor of multiple receptor tyrosine kinases used for the treatment of patients with advanced HCC. Although lenvatinib has been proven effective in treating HCC patients, clinical data show that the response rate to lenvatinib is very low and that 76% of HCC patients are insensitive to lenvatinib. Phenformin is a well-known activator of adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK), which has recently attracted widespread attention because of its anticancer effects. We investigated whether phenformin could enhance the efficacy of lenvatinib in treating HCC and, if so, the underlying mechanisms involved in this process.
Methods: The anticancer effects of the combination of phenformin and lenvatinib in HCC cells were assessed in vitro and in vivo. First, colony formation, EdU and MTT assays were conducted to measure the viability of the HCC cells. Flow cytometry was used to assess the cell cycle distribution of HCC cells. Then, western blotting (WB) was performed to detect protein expression in HCC cells after various treatments. Immunoprecipitation-mass spectrometry (IP-MS) and co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) assays were used to determine the interaction relationships of proteins. In addition, a xenograft model was used to analyze the effects of the different treatments on the proliferation of HCC cells. Immunohistochemistry and western blot assays were conducted to investigate the expression of related proteins in the tissues of the xenograft model. Haematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining was used to analyze the toxicity to the livers and kidneys of mice. Western blot assays were used to detect protein expression in human HCC samples.
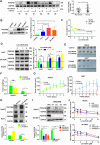
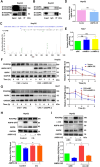
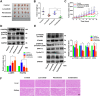
Results: High expression of platelet-derived growth factor receptor β (PDGFRβ) resulted in the insensitivity of HCC cells to lenvatinib, and PDGFRβ knockdown increased the sensitivity of HCC cells to lenvatinib. Phenformin inhibited the proliferation of HCC cells via AMPK-mediated PDGFRβ degradation. Compared with lenvatinib monotherapy, combined treatment with phenformin and lenvatinib considerably enhanced the anticancer effects both in vivo and in vitro. Mechanistic studies showed that AMPK binds PDGFRβ and promotes its degradation via the c-Cbl-mediated lysosomal pathway.
Conclusions: Our study reports a novel combined therapy using phenformin and lenvatinib, which can increase the sensitivity of HCC cells to lenvatinib via AMPK-mediated PDGFRβ degradation. Hence, this treatment strategy may provide a personalized approach for treating HCC patients with high PDGFRβ expression and facilitate the development of basic and clinical research on the use of lenvatinib for the treatment of HCC.
Keywords: AMPK; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Lenvatinib; PDGFRβ; Phenformin.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Vogel A, Meyer T, Sapisochin G, Salem R, Saborowski A. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2022;400(10360):1345–62. - PubMed
-
- Ohri N, Kaubisch A, Garg M, Guha C. Targeted therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2016;26(4):338–43. - PubMed
-
- Zhu Y, Sun P, Wang K, Xiao S, Cheng Y, Li X, et al. Efficacy and safety of lenvatinib monotreatment and lenvatinib-based combination therapy for patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective, real-world study in China. CANCER CELL INT. 2021;21(1):503. 10.1186/s12935-021-02200-7 - PMC - PubMed
