Moderate agreement between the spot albumin‒Creatinine ratio (ACR) and urine albumin (UA) among virally suppressed adults living with HIV in botswana: a cross sectional study
- PMID: 41107861
- PMCID: PMC12534948
- DOI: 10.1186/s12981-025-00809-6
Moderate agreement between the spot albumin‒Creatinine ratio (ACR) and urine albumin (UA) among virally suppressed adults living with HIV in botswana: a cross sectional study
Abstract
Background: Albuminuria predicts end-organ dysfunction in the general population. Its detection in people living with HIV (PLWH) is understudied, despite their heightened risk for end-organ dysfunction. We assessed agreement between albumin‒creatinine ratio (ACR) and urine albumin (UA) tests for albuminuria in a cohort of PLWH in Botswana, where females are more affected by HIV than males.
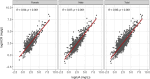
Methods: We used cross-sectional convenience sampling to enrol 1533 virally suppressed adults aged ≥ 21 years who were receiving antiretroviral therapy (ART) in Gaborone, Botswana. We measured urine creatinine levels using a colorimetric assay (Jaffe method) and UA levels using an immunoturbidimetric assay. The UA was used due to it being less costly and simpler, making it more feasible for routine use in resource-limited settings compared to the ACR. We defined albuminuria as 30mg/g versus 30 mg/Lusing ACR and UA levels respectively. Agreement between the two tests was assessed using Cohen's kappa for the entire cohort and then separately by sex groups. The optimal UA cut-off point that matched the sex-specific ACR was assessed using Youden's J index.
Results: The ACR detected similar proportion of participants with albuminuria as UA test (17.1% versus 17.6%). There was moderate agreement in the detection of albuminuria using the ACR versus UA test in the entire cohort, among males and females with Kappa statistics of 0.71 (95% CI: 0.67, 0.76; P < 0.001), 0.74 (95% CI: 0.68, 0.80; P < 0.001), and 0.68 (95% CI: 0.60, 0.76; P < 0.001) respectively. Using Youden's J, the optimal cut points for UA levels were 17.9 mg/L (sensitivity = 88.9%, specificity = 87.3%, AUC = 0.94), 25.0 mg/L (sensitivity = 90.4%, specificity = 90.1%, AUC = 0.94) and 15.1 mg/L (sensitivity = 89.7%, specificity = 87.5%, AUC = 0.94) for the entire cohort, males only and females only, respectively.
Conclusion: UA and ACR show moderate agreement overall. Optimal UA cutoffs differ slightly by sex, suggesting tailored thresholds may improve detection. Future studies should explore clinical indication(s) for using the ACR versus UA levels among PLWH.
Keywords: Albumin-creatinine ratio; Albuminuria; Cardiovascular disease; People living with HIV.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study protocol, informed consent, and other materials were reviewed and approved by the ethics boards of the University of Botswana and the Health Research and Development Committee (IRB of the Botswana Ministry of Health) (HPDME 13/18/1 × 1). All study participants provided written informed consent prior to study procedures. All study procedures were performed according to the IRB approval in accordance with the principles the Declaration of Helsinki. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical