Comparative effects of enteral nutrition strategies on nutritional indices, inflammatory factors, and clinical outcomes in patients with severe traumatic brain injury
- PMID: 41113035
- PMCID: PMC12531519
- DOI: 10.62347/QROO6899
Comparative effects of enteral nutrition strategies on nutritional indices, inflammatory factors, and clinical outcomes in patients with severe traumatic brain injury
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the effects of different enteral nutrition (EN) strategies on nutritional status, inflammatory factors, immune markers, coagulation function, and clinical outcomes in patients with severe traumatic brain injury (sTBI).
Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted on 121 sTBI patients treated at Yiwu Central Hospital between January 2023 and January 2025. Among them, 58 received early EN alone (control group) and 63 received early EN with probiotics (study group). Pre- and post-treatment comparisons between the two groups included: nutritional indices (total protein [TP], albumin [ALB], and prealbumin [PA]), inflammatory factors (interleukin-6 [IL-6], C-reactive protein [CRP], and tumor necrosis factor-α [TNF-α]), immune-related markers (immunoglobulin A [IgA], IgG, and IgM), coagulation indicators (fibrinogen [Fib] and D-dimer [D-D]) and clinical outcomes (Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II (APACHE-II) scores, Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) scores, incidence of complications, time to first defecation, and time to target feeding volume [TFV]).
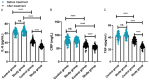
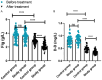
Results: Following treatment, the study group demonstrated significantly smaller reductions in TP and ALB, greater increases in PA, and more pronounced decreases in IL-6, CRP, and TNF-α (all P<0.05). IgA, IgG, and IgM rose more significantly, and Fib and D-D decreased more in the study group (all P<0.05). Clinical outcomes improved significantly, including better APACHE II and GCS scores, earlier defecation and TFV times, and fewer intestinal complications (4.76% vs. 17.24%, P=0.015), with no significant difference in infectious complications.
Conclusion: Early EN combined with probiotics significantly improved nutrition, reduced inflammation, enhanced immune and coagulation function, and improved recovery in sTBI patients.
Keywords: Enteral nutrition; clinical outcome; coagulation function; immune markers; inflammatory factors; nutritional indices; severe traumatic brain injury.
AJTR Copyright © 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures





References
-
- Jin T, Lian W, Xu K, Liu Y, Xu Z, Lu R, Liu M. Effect of combination invasive intracranial pressure (ICP) monitoring and transcranial Doppler in the treatment of severe craniocerebral injury patients with decompressive craniectomy. Ann Palliat Med. 2021;10:4472–4478. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
