Multi-omics analyses integration reveals a novel TRF2-miR-181a-5p-S100A10 regulatory axis in colon cancer
- PMID: 41116155
- PMCID: PMC12536529
- DOI: 10.1186/s11658-025-00813-8
Multi-omics analyses integration reveals a novel TRF2-miR-181a-5p-S100A10 regulatory axis in colon cancer
Abstract
Background: The Telomeric repeat-binding factor 2 (TRF2) binds to TTAGGG repeats located at chromosomes ends and ensures telomere protection together with the other members of shelterin. In addition to its well-known role in telomere maintenance, TRF2 can also bind to interstitial telomeric sequences and regulate the expression of specific genes with a consequent impact on tumor formation and progression. However, a comprehensive analysis of the impact of TRF2 on global gene expression of human cancer cells and of the underlying mechanisms is still lacking.
Methods: The integration of omics technologies (RNA sequencing (RNA-seq), chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP-seq), interactomics, and microRNA (miRNA) profiling) was used to deeply investigate the extra-telomeric role of TRF2. Differential gene expression and binding sites of TRF2 were confirmed by qRT-PCR while the interaction of TRF2 with TATA-box binding protein associated factor 15 (TAF15) was validated by immunoprecipitation and proximity ligation assay. Finally, target specificity was assessed by luciferase assay and western blotting while biological effects were investigated by cell migration analysis (unpaired t tests was used to calculate statistical significance).
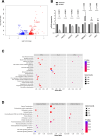
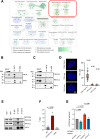
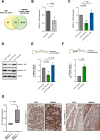
Results: We found that TRF2 impinges on the expression of 717 genes involved in various cancer-related pathways. Unexpectedly, just a small portion of Differentially Regulated genes are directly bound by TRF2, suggesting the existence of alternative mechanisms of TRF2-mediated gene regulation. In particular, we found that TRF2 binds to various noncoding RNA regions and interacts with many RNA binding proteins, supporting TRF2's involvement in noncoding RNA-mediated mechanisms. Through the intersection of omics-analyses, we provided here experimental evidence of a multilayered mechanism of regulation where TRF2, interacting with TAF15, regulates miR-181A1 host gene and mature miR-181a-5p expression, which in turn targets S100A10, a known plasma membrane protein with oncogenic role.
Conclusions: Our work shows, for the first time, a broad overview on the extra-telomeric role of TRF2 in human cancer, further revealing a new axis through which TRF2 contributes to cancer progression.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; S100A10; TAF15; TRF2; miR-181a-5p.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent to publication: All authors have read the manuscript and provided their consent for the submission. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- de Lange T. Shelterin-mediated telomere protection. Annu Rev Genet. 2018;52:223–47. 10.1146/annurev-genet-032918-021921. - PubMed
-
- Broccoli D, Smogorzewska A, Chong L, de Lange T. Human telomeres contain two distinct Myb-related proteins, TRF1 and TRF2. Nat Genet. 1997. 10.1038/ng1097-231. - PubMed
-
- Bilaud T, Brun C, Ancelin K, Koering CE, Laroche T, Gilson E. Telomeric localization of TRF2, a novel human telobox protein. Nat Genet. 1997. 10.1038/ng1097-236. - PubMed
-
- Celli GB, de Lange T. DNA processing is not required for ATM-mediated telomere damage response after TRF2 deletion. Nat Cell Biol. 2005;7:712–8. 10.1038/ncb1275. - PubMed
-
- Denchi EL, De Lange T. Protection of telomeres through independent control of ATM and ATR by TRF2 and POT1. Nature. 2007;448:1068–71. 10.1038/nature06065. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

