Comparative Evaluation of Imaging Modalities for Complex Oral and Maxillofacial Pathologies: A Systematic Review and Semi-Quantitative Synthesis
- PMID: 41116929
- PMCID: PMC12535666
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.92681
Comparative Evaluation of Imaging Modalities for Complex Oral and Maxillofacial Pathologies: A Systematic Review and Semi-Quantitative Synthesis
Abstract
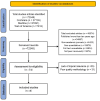
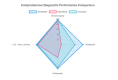
It has been established that a significant section of the population is affected by oral and maxillofacial pathologies. This systematic review and semi-quantitative synthesis, therefore, aim to identify different imaging modalities that are used to diagnose these pathologies and their relative effectiveness. This study also evaluates the impact of technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) on the efficacy of the imaging modalities. The method applied in the study was a systematic review and semi-quantitative synthesis, and different quantitative studies were selected and their findings analyzed. The selection process was non-biased in nature since objective inclusion and exclusion criteria, such as the year the study was published and the rating of the methodology, were used in the selection process. The study found that certain imaging modalities, such as ultrasonography and scintigraphy, have more accuracy and sensitivity compared to conventional radiology. Ultrasonography was also found to have more advantages due to its lack of use of ionization, thus reducing the impact associated with ionization during the imaging process. AI was also found to have a positive impact on different imaging modalities, as it increased the sensitivity and the accuracy of the modalities. One of the recommendations is continued research on the impact of AI tools; technologies are continually being improved, and therefore, their effectiveness is likely to increase over time. The use of ultrasonography should be advocated for, and the necessary resources should be made available, as ultrasonography not only has a higher rate of success but also reduces the risks associated with conventional imaging processes.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; diagnostic accuracy; imaging modalities; oral and maxillofacial pathologies; ultrasonography.
Copyright © 2025, Alowaimer et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures




References
-
- The global, regional, and national burden of oral disorders in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2021, and projections to 2050: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021 (Preprint) Wang S, Li J, Jiang J, Liu N, Xiao Y, Liu J. Lancet. 2021
-
- Advanced diagnostic methods in oral and maxillofacial pathology. Part I: molecular methods. Jordan RC, Daniels TE, Greenspan JS, Regezi JA. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2001;92:650–669. - PubMed
-
- Performance of different imaging techniques in the diagnosis of head and neck cancer mandibular invasion: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Qiao X, Liu W, Cao Y, et al. Oral Oncol. 2018;86:150–164. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
