Identification of stigmasterol derived AChE inhibitors for Alzheimer's disease using high throughput virtual screening and molecular dynamics simulations
- PMID: 41120520
- PMCID: PMC12541016
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-20527-3
Identification of stigmasterol derived AChE inhibitors for Alzheimer's disease using high throughput virtual screening and molecular dynamics simulations
Abstract
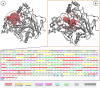
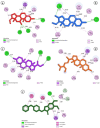
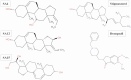
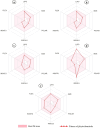
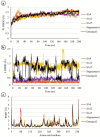
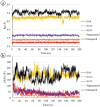
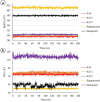
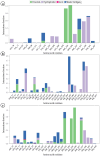
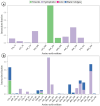
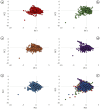
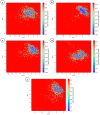
Alzheimer's disease (AD), a progressive neurodegenerative disorder, poses a significant global health burden due to its intricate pathology and the absence of curative treatments. Current therapies primarily offer symptomatic relief, often with limited efficacy and complications, thereby underscoring the urgent need for innovative, safer, and more effective interventions. Stigmasterol, a plant-derived phytosterol, has demonstrated neuroprotective properties, including anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects, which positions this sterol as a compelling candidate for further investigation in AD treatment. In this investigation, high-throughput virtual screening of 972 stigmasterol analogs (SAs) was conducted to identify potential acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitors, followed by ADMET filtering, molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, MM/GBSA free binding energy estimations, and DFT calculations. Three lead compounds, including SA4 (-10.9 kcal/mol), SA12 (-10.6 kcal/mol), and SA15 (-10.5 kcal/mol), demonstrated superior binding affinities compared to stigmasterol (-9.6 kcal/mol) and the control drug donepezil (-8.6 kcal/mol). Docking interaction analysis revealed strong binding by hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic interactions, whereas pharmacokinetic, pharmacodynamic, and toxicity assessments confirmed the favorable characteristics of these compounds. MD simulations (200 ns) demonstrated the structural compactness of the compounds, which was further supported by principal component analysis and Gibbs free energy landscape experiments. MM/GBSA identified SA4 as the most potent analog (-82.21 kcal/mol), followed by SA15 (-80.40 kcal/mol) and SA12 (-69.72 kcal/mol). A DFT-based molecular reactivity analysis revealed decreased reactivity and increased kinetic stability of the lead candidates in their transition from free to bound states. These findings provide insights into the therapeutic potential of stigmasterol analogs as AChE inhibitors, thus offering the groundwork for in vivo and in vitro validation for advancing AD treatment.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s; DFT; HTVS; MD simulation; MM/GBSA; Stigmasterol.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Gaudreault, R. & Mousseau, N. Mitigating alzheimer’s disease with natural polyphenols: A review. Curr. Alzheimer Res.16 (6), 529–543. 10.2174/1567205016666190315093520 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Akıncıoğlu, H. & Gülçin, İ. Potent acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: potential drugs for alzheimer’s disease. Mini Rev. Med. Chem.20 (8), 703–715. 10.2174/1389557520666200103100521 (2020). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

