SHIPi improves hematologic recovery after chemotherapy
- PMID: 41120849
- PMCID: PMC12538841
- DOI: 10.1186/s10020-025-01383-3
SHIPi improves hematologic recovery after chemotherapy
Abstract
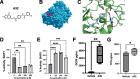
The use of recombinant growth factors has led to improved hematopoietic function after chemotherapy, but hematologic and immune complications still occur after chemotherapy which can be life-threatening. Here we show that pan-SHIPi compounds can induce endogenous G-CSF and TPO production in vivo and can also increase host survival after a lethal fungal challenge. In addition, we show that consistent with their ability to induce G-CSF, pan-SHIPi compounds can promote increased granulopoiesis in normal mice and speed recovery of neutrophil counts after chemotherapy. We also report the identification of a novel SHIP1-selective inhibitor, A32, that also increases steady state production of both G-CSF and TPO. These findings indicate small molecule inhibitors of SHIP1 can promote hematologic recovery after myeloablative chemotherapy and are a unique means to induce endogenous production of multiple growth factors that promote hematologic recovery.
Keywords: 5-FU; A32; Candida albicans; Chemotherapy; K161; Neutrophils; SHIP1; SHIPi.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All studies using mice were approved by the IACUC at SUNY Upstate. Any other ethical approvals are not applicable. Consent for publication: All authors have been advised of publication of this work and none have opposed. No other consents are needed. Competing interests: W.G.K, S.F., C.P., C.D.S., D.S. and J.D.C have patents, pending and issued, concerning the analysis and targeting of SHIP1 and SHIP2 in disease and infection. The other authors have no interests to declare.
Figures

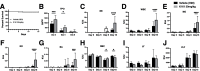
References
-
- Chowdhury BP, et al. SHIP1 inhibition via 3-alpha-amino-cholestane enhances protection against Leishmania infection. Cytokine. 2023;171:156373. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

