CD19 CAR T-Cell Therapy in Richter Transformation: A Multicentre Retrospective Analysis by the European Research Initiative on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia
- PMID: 41123167
- PMCID: PMC12541669
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.70841
CD19 CAR T-Cell Therapy in Richter Transformation: A Multicentre Retrospective Analysis by the European Research Initiative on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia
Abstract
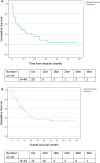
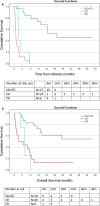
Richter transformation (RT) is a serious complication of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL), with poor outcomes. While CAR T-cells have shown promise in large B-cell lymphoma, their efficacy in RT remains unclear, and the role of allogeneic stem cell transplant (alloSCT) post-CAR T-cells has not been established. This study aimed to assess the clinical response and survival of patients with RT treated with anti-CD19 CAR T-cells. This retrospective multicentre study, conducted by the European Research Initiative on CLL (ERIC), included patients with RT who received anti-CD19 CAR T-cells between 06/2018 and 01/2024. Progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were evaluated from CAR T-cell infusion. Fifty-four patients with RT were treated with anti-CD19 CAR T-cells (academic products, n = 29; commercial products, n = 25). The median age was 63 years, with 72% having an ECOG performance status (PS) of 0 to 1. Seven patients (13%) underwent alloSCT following CAR T-cell infusion, with the indications being consolidation therapy (n = 4) and relapse/progression (n = 3). The overall response rate was 65%, with 46% achieving complete response (CR) at 1 month and 50% at 3 months. The median PFS was 8.0 months (95% CI: 2.1-13.8) and the median OS was 14.4 months (95% CI: 8.8-19.2). The median PFS was 31.6 months for patients achieving CR at 1 or 3 months post CAR T-cells. Significant factors associated with mortality included high ECOG PS (p < 0.001), high LDH at CAR T infusion (p = 0.005), ICANS (p = 0.046) and no response at 1 month (p = 0.02). Multivariable Cox regression analysis identified treatment response at 1 month (p = 0.001) and increasing age (p = 0.5) as significant predictors of mortality. This study shows encouraging response rates and manageable toxicity for patients with RT treated with both academic and commercially available CAR T-cell products.
Keywords: CAR‐T cells; Richter transformation; allogeneic SCT.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
O.B.‐K. and R.R.—Honorarium from novartis and gilead. M.R.—Vittoria Biotherapeutics: Current equity holder in private company, Patents and Royalties; AbClon Inc.: Other: Consultancy, Research Funding. S.G.—Gilead, Medison, MSD, Novartis, Sanofi, Takeda: Consultancy. A.V.—attended scientific advisory boards organised by Johnson & Johnson, Abbvie, Astrazeneca, BeiGene and Takeda; Speaker Bordeaux for Johnson & Johnson and Abbvie. A.A.—Karyospharm: Research Funding; Ascentage: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; BeiGene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Bristol Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; A0bbVie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Eli Lilly: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other, Speakers Bureau; TG Therapeutics: Consultancy; Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel, accommodations, expenses, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau. V.O.‐M.—Pfizer: Honoraria; Kite/Gilead: Honoraria, Other: Travel grants; Miltenyi: Honoraria; Hospital Clínic de Barcelona: Current Employment; Janssen: Honoraria, Other: Travel grants; Celgene‐BMS: Honoraria, Other: Travel grants; Novartis: Honoraria. G.G.—Vittoria Biotherapeutics: Honoraria. B.A.—Sanofi: Consultancy; Johnson and Johnson: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; MSD: Consultancy; Takeda: Consultancy; Medison: Consultancy. T.T.—Janssen, Roche, Abbvie, Astra, Takeda, Novartis, Beigene, Medison: Consultancy, Research Funding. L.S.—Janssen: Honoraria; Lilly: Honoraria; BeiGene: Honoraria; AstraZeneca: Honoraria; AbbVie: Honoraria; Octapharma: Honoraria. K.S.—AstraZeneca: Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Roche: Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Honoraria; AbbVie: Honoraria, Research Funding; Lilly: Honoraria. T.C.—Honoraria from AbbVie, AstraZeneca and BeiGene. P.G.—Loxo@Lilly: Consultancy; Galapagos: Consultancy; Johnson&Johnson: Consultancy, Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Research. unding; BeiGen: Consultancy; AstraZeneca: Consultancy, Research Funding; AbbvVie: Consultancy, Research Funding; MSD: Consultancy; Galapagos: Consultancy; Roche: Consultancy. O.B., J.D., E.V., M.G., A.S., R.S., R.M., S.J.S., L.P., T.Z., R.F., O.A., N.M.C., G.G., R.Y., A.N., R.L., I.D., E.M., N.S.‐T. declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Neelapu S. S. and Ghobadi A. J. C. A., “2‐Year Follow‐Up and High‐Risk Subset Analysis of Zuma‐1, the Pivotal Study of Axicabtagene Ciloleucel (Axi‐Cel) in Patients With Refractory Large B Cell Lymphoma,” Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation 25 (2019): S65.
-
- Schuster S. J., Bishop M. R., Tam C. S., et al., “Tisagenlecleucel in Adult Relapsed or Refractory Diffuse Large B‐Cell Lymphoma,” New England Journal of Medicine 380, no. 1 (2019): 45–56. - PubMed
-
- Abramson J. S., Palomba M. L., Gordon L. I., et al., “Lisocabtagene Maraleucel for Patients With Relapsed or Refractory Large B‐Cell Lymphomas (TRANSCEND NHL 001): A Multicentre Seamless Design Study,” Lancet 396, no. 10254 (2020): 839–852. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

