Uncertain climate effects of anthropogenic reactive nitrogen
- PMID: 41125789
- PMCID: PMC12545199
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-09337-9
Uncertain climate effects of anthropogenic reactive nitrogen
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The research project that has funded most of this work has received funding (approximately 25% of the total budget) from industry partners who have an interest in green or blue ammonia.
Figures


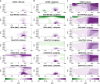
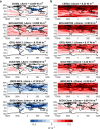
Comment on
-
Global net climate effects of anthropogenic reactive nitrogen.Nature. 2024 Aug;632(8025):557-563. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07714-4. Epub 2024 Jul 24. Nature. 2024. PMID: 39048828 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Szopa, S. et al. in Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis (eds Masson-Delmotte, V. et al.) 817–922 (IPCC, Cambridge Univ. Press, 2021).
-
- Gliss, J. et al. AeroCom phase III multi-model evaluation of the aerosol life cycle and optical properties using ground- and space-based remote sensing as well as surface in situ observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys.21, 87–128 (2021).
-
- Bian, H. S. et al. Investigation of global particulate nitrate from the AeroCom phase III experiment. Atmos. Chem. Phys.17, 12911–12940 (2017).
-
- Berglen, T. F., Berntsen, T. K., Isaksen, I. S. A. & Sundet, J. K. A global model of the coupled sulfur/oxidant chemistry in the troposphere: the sulfur cycle. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos.10.1029/2003jd003948 (2004).

