A systematic literature review on mammography: deep learning techniques for breast cancer detection with global and Asian perspectives
- PMID: 41126088
- PMCID: PMC12542462
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-025-14876-5
A systematic literature review on mammography: deep learning techniques for breast cancer detection with global and Asian perspectives
Abstract
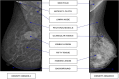
Purpose: Breast cancer remains a leading cause of mortality in women worldwide, with notable disparities in incidence and prognosis across regions. This systematic review explores the application of Deep Learning-based computer-aided diagnostic (CAD) systems for breast cancer detection, with a special focus on Asia to highlight underrepresented perspectives and challenges.
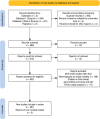
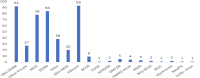
Methods: We conducted a systematic Literature review in accordance with PRISMA guidelines. A comprehensive search of Scopus and Web of Science databases was performed to identify relevant studies published between January 2018 and November 2023, with an additional hand search for recent studies from 2024 to 2025. After screening 1051 records, 287 articles were included based on predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria. Quality assessment focused on the relevance of deep learning-based approaches to mammographic breast cancer detection, emphasizing global research trends and focused analysis of studies involving Asian populations.
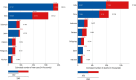
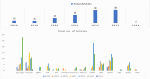
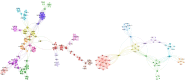
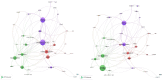
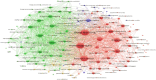
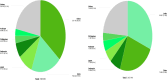
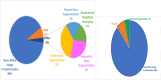
Results: The review identified major research trends in deep learning-based mammographic analysis, with most studies focusing on lesion classification while comparatively fewer addressed detection, segmentation, and breast density assessment. Studies using Asian datasets revealed unique challenges, including higher breast density, limited annotations, and under-representation in public datasets. Analysis of methodologies highlighted varied use of image preprocessing and augmentation techniques. Focus maps were used to visualize contributions across tasks and populations, revealing gaps in multi-class BI-RADS classification and a global research bias toward Caucasian datasets (> 80%).
Conclusion: This review reveals that most deep learning models for breast cancer detection are trained predominantly on Caucasian datasets, creating significant limitations when applied to other populations due to demographic differences in breast density and imaging characteristics. To improve breast cancer screening globally, researchers must develop deep learning systems using diverse datasets that represent different populations, validate these models across various ethnic groups, and ensure clinical testing includes women from multiple demographic backgrounds.
Systematic review registration: PROSPERO CRD 42,023,478,896.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Asian; Breast cancer; Deep learning; Global trend; Mammograms; Mammography; Systematic literature review.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: No empirical research involving humans or animals conducted by any authors is included in this paper. All the data involved in this study were extracted from published articles. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Code availability: Not applicable
Figures


References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2023;73(1):17–48. - PubMed
-
- Globocan 2022 factsheet.: Globocan 2020 fact sheets. Accessed February 25. 2024. Available from: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/populations/935-asia-fact-shee...
-
- Cytecare T. Statistics of breast cancer in India: Cytecare Hospitals. Cytecare Hospital in Bangalore. Accessed December 23, 2023. Available from: https://cytecare.com/blog/breast-cancer/statistics-of-breast-cancer/
-
- Maurya AP, Brahmachari S.Current status of breast cancermanagement in India. Indian JSurg. 2020(S2). 10.1007/s12262-020-02388-4.
-
- Singh T, Khandelwal N, Singla V, Kumar D, Gupta M, Singh G, et al. Breast density in screening mammography in Indian population-is it different from Western population? Breast J. 2018;24(3):365–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

