Sclerostin's role in bone-muscle crosstalk and osteoporosis pathogenesis
- PMID: 41127352
- PMCID: PMC12537467
- DOI: 10.1016/j.afos.2025.06.004
Sclerostin's role in bone-muscle crosstalk and osteoporosis pathogenesis
Abstract
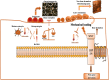
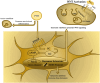
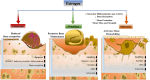
This review examines sclerostin, a critical regulator of Wnt signaling, focusing on its role in bone homeostasis and its emerging involvement in muscle-bone crosstalk. It examines the regulatory influence of hormones, mechanical stress, and myokines on sclerostin expression under both physiological and pathological conditions. Recent advances underscore sclerostin's role in osteoporosis pathogenesis and its involvement in bone remodeling, while also revealing its emerging significance in muscle-bone communication. Despite these insights, the underlying mechanisms of its regulation remain incompletely understood. By consolidating recent research, this review provides a comprehensive perspective on sclerostin's multifaceted roles and their implications for bone and muscle health.
Keywords: Crosstalk; Molecular interaction; Myokines; Osteoporosis; Regulators; Sclerostin.
© 2025 The Korean Society of Osteoporosis. Publishing services by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Chatterjee A., Paul S., Bisht B., Bhattacharya S., Sivasubramaniam S., Paul M.K. Advances in targeting the WNT/β–catenin signaling pathway in cancer. Drug Discov Today. 2022;27:82–101. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

