Impact of open markets on zoonotic threats and antimicrobial resistance: A One Health concern
- PMID: 41127627
- PMCID: PMC12538495
- DOI: 10.1016/j.onehlt.2025.101228
Impact of open markets on zoonotic threats and antimicrobial resistance: A One Health concern
Abstract
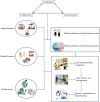
Open markets play a significant role in global food distribution, particularly in East and Southeast Asia, where fresh produce, seafood, and live animals are commonly sold. However, they pose significant public health risks by facilitating the transmission of zoonotic pathogens and contributing to the spread of antimicrobial resistance (AMR). High human-animal interactions, poor hygiene, and unregulated antimicrobial use contribute to the emergence and spread of resistant microorganisms. Despite these risks, the role of open markets in the spread of zoonotic pathogens and AMR has received limited attention. Thus, this review explores the possible mechanisms by which AMR may spread in open markets, the role of microbial genetic exchanges in the emergence of new resistant strains in these settings, and the zoonotic risks associated with the live animal trade. It also discusses strategies and future directions to mitigate these issues, emphasizing the urgency of taking the required One Health actions to minimize the spread of AMR and the zoonotic infections globally. These actions should include robust surveillance, regulatory measures, public health initiatives along with advocacy and training, all crucial for protecting global health.
Keywords: Antimicrobial resistance; Mitigation strategies; One health approaches; Open market; Public health risks; Transmission patterns; Zoonosis.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The author reports no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Qasim S., Khan A.U., Raza A. Zoonotic diseases and antimicrobial resistance: a dual threat at the human-animal interface. Arch. Vet. Med. 2024;17:5–17. doi: 10.46784/E-AVM.V17I1.361. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources