NFC/RFID-enabled wearables and implants for biomedical applications
- PMID: 41130975
- PMCID: PMC12549948
- DOI: 10.1038/s41378-025-01010-5
NFC/RFID-enabled wearables and implants for biomedical applications
Abstract
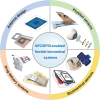
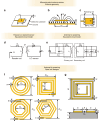
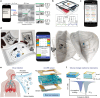
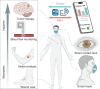
Near Field Communication (NFC) and Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technologies offer wireless data transmission and energy supply for flexible wearable and implantable sensing systems. By eliminating bulky batteries or external wiring, these technologies significantly advance personalized medicine through wearable and implantable systems with reduced size, increased flexibility, and improved mechanical adaptability to the human body. This multidisciplinary research area encompasses the fundamental mechanisms of antenna theory, simulation & design, micro/nano-fabrication, and their biomedical applications. This review provides an overview of emerging wireless, personalized/decentralized biomedical devices focusing on NFC/RFID antennas design mechanisms, flexible NFC/RFID-based physical, chemical, and biosensors, as well as drug delivery implants. Moreover, challenges and future directions regarding flexible NFC/RFID-based systems are provided. Advancing this field will require collaborative efforts from researchers in antenna design, materials science, biology, and medical care, driving the development of NFC/RFID in biomedical applications.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Zhang, P., Zhu, B., Du, P. & Travas-Sejdic, J. Electrochemical and electrical biosensors for wearable and implantable electronics based on conducting polymers and carbon-based materials. Chem. Rev.124, 722–767 (2024). - PubMed
-
- Kim, J. et al. A soft and transparent contact lens for the wireless quantitative monitoring of intraocular pressure. Nat. Biomed. Eng.5, 772–782 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Kwon, K. et al. A battery-less wireless implant for the continuous monitoring of vascular pressure, flow rate and temperature. Nat. Biomed. Eng.7, 1215–1228 (2023). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

