LC/ESI-MS/MS phytochemical profiling and apoptotic effect of Haloxylon scoparium leaf extract on hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 41131348
- PMCID: PMC12549966
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-21041-2
LC/ESI-MS/MS phytochemical profiling and apoptotic effect of Haloxylon scoparium leaf extract on hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
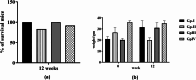
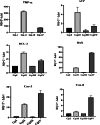
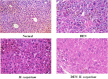
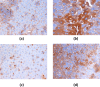
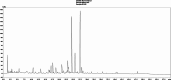
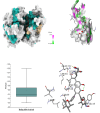
Haloxylon scoparium, a plant native to Moroccan Sahara, was investigated for its potential anticancer activity against hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The study aimed to evaluate the effects of its methanolic extract on HCC and to conduct detailed chemical analysis using LC-ESI-MS/MS. In vitro cytotoxicity was assessed using HepG2 liver cancer cell line. In vivo experiments involved inducing HCC in mice with diethylnitrosamine (DEN). The study monitored inflammatory (TNF-α), apoptotic (BAX, Caspase-3, Caspase-8), and oncogenic markers (AFP, Bcl-2) through blood and liver tissue analysis. Liver histopathology was also performed to evaluate tissue-level changes. Mice survival rates were 83.33% in the DEN group and 91.67% in the DEN/H. scoparium group. Liver function markers (TBILR, ALP, AST) significantly decreased in the treatment group. TNF-α levels, elevated in DEN-only mice, were notably reduced after treatment. Oncogenic markers showed significant elevation in the DEN group but were decreased in the treatment group, whereas apoptotic markers were significantly elevated after treatment. Histopathology revealed more preserved liver architecture and scattered apoptotic foci in treated mice. Phytochemical profiling identified 27 compounds, including organic acids, phenolic acid derivatives, and flavonoids by LC/ESI-MS/MS. Molecular docking using AutoDock MGLTools 1.5.7 showed strong binding affinities of quercetin and isorhamnetin glycosides with cancer-related proteins (BCL-2, BAX, Caspases, AFP, TNF-α), supporting experimental results. 3D interaction models and box plots confirmed the stability and specificity of ligand-protein interactions. The study concludes that H. scoparium extract demonstrates promising multi-target anticancer potential and may serve as a valuable candidate for pharmaceutical development.
Keywords: Haloxylon scoparium; In silico study; Good health and well-being; Hepatocellular carcinoma; LC/ESI-MS/MS; Polyphenols; TNF-α.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Compliance with ethical standards: All procedures in this study, including handling, anesthesia, and sacrifice, adhered to the ethical guidelines approved by the Ethical Committee of the Federal Legislation and the National Institutes of Health Guidelines in the United States. All animal experiments were carried out under Institutional Ethical Committee rules for the care and use of experimental animals, which were authorized by Theodor Bilharz Research Institute’s Animal Ethics Committee in Giza, Egypt (FWA 00010609). All methods are documented in line with the ARRIVE guidelines for reporting animal experiments. ( https://arriveguidelines.org ). Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Boucherit, H. & Benaradj, A. Therapeutic properties of the woody plant Haloxylon scoparium Pomel in the steppe region of Naâma (Algeria). Biodivers. Res. Conserv.72, 39–46 (2024).
-
- Amtaghri, S. & Eddouks, M. Comprehensive review on the genus Haloxylon: Pharmacological and phytochemical properties. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord Drug Targets. 24, 1146–1160 (2024). - PubMed
-
- Bouaziz, A. et al. Antibacterial and antioxidant activities of Hammada scoparia extracts and its major purified alkaloids. S Afr. J. Bot.105, 89–96 (2016).
-
- Ebrahim, A. M., Idris, A. M., Alnajjar, A. O. & Michalke, B. Cr and Mn total, accessible species, and protein-fraction contents in plants used for traditional anti-diabetes treatment. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol.62, 126645 (2020). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

