Correlations of biochemical and clinical outcomes with 10-year results after robotic stereotactic body radiotherapy for localized prostate cancer
- PMID: 41131547
- PMCID: PMC12548164
- DOI: 10.1186/s13014-025-02739-z
Correlations of biochemical and clinical outcomes with 10-year results after robotic stereotactic body radiotherapy for localized prostate cancer
Abstract
Background: Long-term data on the efficacy of robotic stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for localized prostate cancer (LPC) remain limited. This study aimed to evaluate the 10-year treatment outcomes of SBRT in LPC patients and identify key prognostic factors.
Methods: A total of 82 patients with LPC who underwent five-fraction SBRT (doses of 35-37.5 Gy) were included. The median follow-up duration was 11.0 years (range, 3.3-15.9 years). Clinical outcomes, including the biochemical failure-free survival (BCFFS), clinical failure-free survival (CFFS), and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) kinetics, were analyzed to evaluate the impact of various clinical and treatment factors on prognosis.
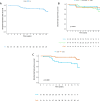
Results: The 10-year BCFFS and CFFS rates were 86.3% (95% confidence interval [CI], 78.6-94.8) and 86.7% (95% CI, 78.8-95.4), respectively. Nine cases of biochemical failure were observed, alongside local (n = 1), regional (n = 2), and distant (n = 5) metastases. The cancer-specific survival rate was 100%. The median PSA nadir was 0.09 ng/ml (range, 0.0-3.12 ng/ml) and the median interval to PSA nadir was 52.8 months (range, 0.4-170.2 months). There was a negative correlation between the time to the PSA nadir and the PSA nadir value (r = -0.233, p = 0.035). Daily SBRT was associated with improved BCFFS compared to every-other-day treatment (hazard ratio [HR], 0.220; 95% CI, 0.067-0.720; p = 0.012), while a longer interval to PSA nadir (≥ 5 years) was associated with better CFFS (HR, 0.120; 95% CI, 0.015-0.944; p = 0.044).
Conclusions: Robotic SBRT for LPC demonstrates durable long-term efficacy. Daily treatment schedules and interval to PSA nadir were identified as crucial prognostic indicators. These findings highlight the importance of PSA kinetics in predicting treatment success following robotic SBRT.
Keywords: Biochemical failure-free survival; Clinical failure-free survival; Nadir; Prostate cancer; Prostate-specific antigen; Stereotactic body radiotherapy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of all participant institutions and conducted in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Informed consent was not required as the study involved a retrospective review with minimal risk to the participants. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Jackson WC, Silva J, Hartman HE, Dess RT, Kishan AU, Beeler WH, et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for localized prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of over 6,000 patients treated on prospective studies. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2019;104:778–89. 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2019.03.051. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dasu A, Toma-Dasu I. Prostate alpha/beta revisited – an analysis of clinical results from 14 168 patients. Acta Oncol. 2012;51:963–74. 10.3109/0284186X.2012.719635. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

