HCB101: a novel potent ligand-trap Fc-fusion protein targeting the CD47-SIRPα pathway with high safety and preclinical efficacy for hematological and solid tumors
- PMID: 41131565
- PMCID: PMC12548202
- DOI: 10.1186/s13045-025-01742-x
HCB101: a novel potent ligand-trap Fc-fusion protein targeting the CD47-SIRPα pathway with high safety and preclinical efficacy for hematological and solid tumors
Abstract
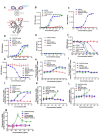
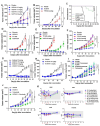
Cluster of differentiation 47 (CD47) delivers an inhibitory signal that suppresses phagocytosis and prevents immune clearance of tumor cells by interacting with signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPα) on myeloid cells. Although blockade of the CD47-SIRPα axis is a promising immunotherapeutic strategy, clinical development has been hindered by on-target toxicities (e.g., severe anemia) and insufficient potency. Herein we report a third generation CD47-SIRPα inhibitor HCB101, a rationally designed SIRPα-Fc fusion protein generated from a large-scale screening of a structure-guided SIRPα extracellular domain (ECD) mutant library and fused to a human IgG4 Fc. HCB101 demonstrates high-affinity binding to CD47, robustly promotes macrophage-mediated phagocytosis of tumor cells without affecting red blood cells and exhibits unique advantages over current CD47-targeting agents, including Hu5F9-G4, TTI-622, and ALX148. In multiple xenograft cancer models, HCB101 induced significant inhibition of tumor growth as a single agent and showed synergistic anti-tumor effects when combined with anti-HER2 or anti-EGFR monoclonal antibodies. Additionally, HCB101 treatment increased the M1/M2 macrophage ratio in the tumor microenvironment, suggesting repolarization of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) toward a pro-inflammatory phenotype. No dose-limiting toxicities or hematologic adverse effects were observed in murine or non-human primate studies.
Keywords: CD47; Cancer immunotherapy.; HCB101; Macrophage; Phagocytosis; SIRP-alpha.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All animal experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of HanchorBio Inc., and conducted in accordance with internal institutional guidelines, the Animal Protection Act, and relevant regulations promulgated by the Council of Agriculture (now Ministry of Agriculture), Taiwan. The non-human primate (NHP) studies, conducted by the CRO (Joinn or WuXi), were specifically reviewed and approved by the IACUC and carried out in certified facilities in mainland China in compliance with local laws and regulations governing the ethical use of laboratory animals, including the Regulations for the Administration of Laboratory Animals, and under strict animal welfare standards. All studies involving human samples were reviewed and approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of the Development Center for Biotechnology (DCB), Taiwan. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants prior to sample collection, in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and the Human Subjects Research Act of Taiwan. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

